This question was very popular among the candidates and the overall performance was well above average except in part (c)(ii).
The expected answers were as follows:
(a) Differences between a sound wave and a radiowave
| Sound wave |
Radio wave |
| is a mechanical wave |
is an electromagnetic wave |
| is longitudinal |
is transverse |
| has speed less than speed of light. |
has speed equal to that of light |
| requires a material medium for propagation/cannot travel through vacuum. |
does not require a material medium for propagation/can travel through vacuum. |
(i)
(b) The vibrating tuning fork forces the table top to vibrate. The table top has a much larger area and is therefore in contact with a larger volume of air undergoing vibration. Hence, sound heard is amplified.
(c) Conditions necessary for:
(i) production of stationary wave
- Two waves must be traveling in opposite directions.
- Incident and reflected waves must have the same frequency/wavelength.
- Incident and reflected waves must have equal amplitude.
- There must be superimposition.
- There must be a barrier
(ii) formation of interference wave pattern
- Two sources must be involved.
- The two sources must be coherent/have a constant phase difference as well as the same frequency and amplitude.
- The waves that are interfering must have the same amplitude
- The distance between the sources must be of the order of the wavelengths of the waves.
(iii) total internal reflection
- The wave must be traveling from a denser medium to a less dense medium
- The angle of incidence of the wave in the denser medium must be greater than the critical angle for the medium.
(d)(i) Diagram
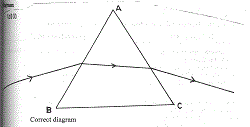
Correct diagram
(ii) Sin (A + dm)
n = 2
2
Sin (A/2)
Sin (60 + 41)
 = 2
= 2
Sin (60/2)
= 1.54



