(a) Majority of the responding candidates gave the correct diagram but the explanation was poorly
rendered.
(b) (i) many candidates gave the correct explanation of standing wave.
(ii) Very few candidates succeeded in giving the correct explanation of persistence of vision.
(c) Many candidates could not differentiate between 'iris' and the 'pupil' ofthe eye. Besides they
could not describe correctly the responses sought.
(d) Performance was average.
The expected responses are:
(a) (i)
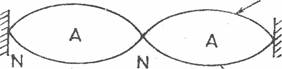
(Reflected wave)
N'
Incident wave).
Correct diagram
N=Node
A = Antinode
(Do not penalize for barriers not shown)
A node is a point on a stationary wave where there is no movement ofthe medium/points
of zero displacement.
OR
A Node is a point of destructive interference
An antinode is a point on a stationary wave where there is maximum displacement of
the medium.
OR
An antinode is a point of constructive interference.
(b)(i) Standing wave occurs when a progressive wave is reflected from a hard surface and
superimposed on the incident wave.
OR
Standing wave occurs when waves of the same frequency and amplitude traveling in
opposite direction are superimposed.
(ii) Persistence of vision is a property of the eye whereby the sensation of vision lasts
for a short but definite time after the object has been removed.
(c)(i) In dim light, the iris contracts increasing the size of the pupil to let in sufficient light.
(ii) In excessive brightness the iris quickly expands in size thus reducing the size of the
pupil which reduces the amount of light entering the eye .
(d)(i) Either y = A sin2Π/λ (x - vt) ....................................... (α)
OR y = A sin[2Πx/λ - 2Πvt/λ ]............................................. (β)
= 0.20 sin (0.40Πx - 0.40Π x 60t) ............... (γ)
Comparing equations (β) and (γ)
2Πx/λ= 0.40Πx
λ = 5 cm
(ii) 2Πvt/λ = 0.40Πx x 60t
v = fλ
2Πvt = 0.40Π x 60t
f = 12Hz



