Most candidates were able to:
- state the operations that are carried out on the surface;
- planing machines;
- state the specific use of the given tools;
- explain kerf bending;
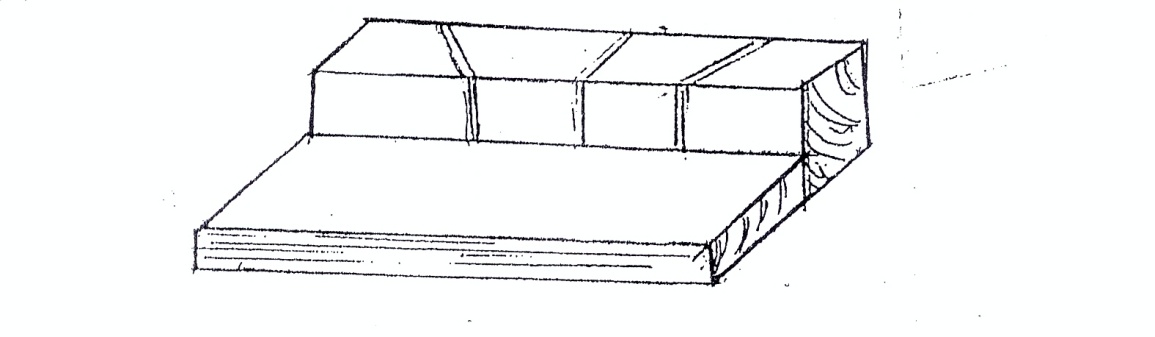
- sketch a mitre block.
However, few candidates were unable to sketch a mitre block.
The expected response to question 1 is as given below:
(a) (i) A timber to be used for wood bending should be:
- surfacing;
- tapering;
- edging;
- splaying;
- rebating;
- bevelling;
- chamfering.
(ii) - Rebating.
(b) (i) Mallet – for driving chisels;
- for assembling joints;
- for separating joints.
(ii) Mitre square – for marking and testing angles at 45o
(iii) Veneer hammer –
- is used for pressing down veneers during gluing;
- is used for squeezing out surplus glue when gluing;
- is used for squeezing out trapped air when veneering.
(iv) Sliding bevel –
- for setting/marking out angles other than 90'
- for setting/marking out dovetails;
- for setting/marking out mitres;
- for setting/marking out bevels.
- for testing angles other than 90'
(c) (i) Kerf bending is the process involving the cutting of a piece of
solid wood on
the inside surface with a series of saw cuts and bending it over pegs to form
a desired shape or curve
(d) MITRE BLOCK