Question 3
(a) Explain four causes of damage to maize during storage. [8 marks]
(b) Two heterozygous tall plants, Tt were crossed in an experiment. Using a
genetic diagram,
(i) show all the possible offspring that could result from this cross. [2 marks]
(ii) determine the:
I. genotypic ratio of the offspring;
II. phenotypic ratio of the offspring. [2 marks]
(c) State Mendel’s first and second laws of inheritance. [4 marks]
(d) Mention two forage grasses. [2 marks]
Observation
Question 3 was not popular among candidates and performance was below average.
(a) Many candidates displayed lack of knowledge of the causes of damage to maize
during storage and responses were poor.
(b) Candidates showed an improvement in questions on genetics because many of them
were able to show the genetic cross as well as determine the genotypic and
phenotypic ratios of the offspring. However, Mendelian laws of inheritance was
poorly answered.
(c) The performance of many candidates in Question 3(d) was abysmal due to wrong
spelling of botanical names of forage grasses as well as failure to adhere to the
scientific convention in writing botanical names.
The expected answers include:
3. (a) Explanation of causes of damage to maize during storage
(i) High humidity
- High humidity often leads to mould formation, thus reducing the quality of maize
(ii) Pests
- The presence of pests reduces the quality of maize
- Pests reduces the quantity of maize
- Reduces the viability of seeds ; thus the germination rate
(iii) Pathogens
- The presence of moulds and other fungi reduces the quality of stored maize
(iv) Heat generated during storage
- This enhances the formation of moulds, thus reducing the quality of maize
(v) Poor Storage Structure:
- Leaking roof allows water to get into the stored maize; thus leading to mouldiness
- Allows infestation of pests and pathogens
(b) (i) Possible offspring that could result from the cross
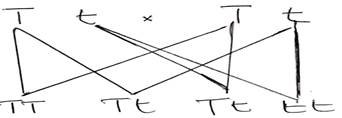
(ii) I. Genotypic ratio of the offspring
1:2:1
II. Phenotypic ratio of the offspring3:1
(c) Mendel’s laws of inheritance
First law (Law of segregation of genes)
Genes occur in pairs and are transmitted independently from one generation to another
Second law (Law of independent assortment of genes)
Genes for different traits are sorted separately from one another such that the
inheritance of one trait is not dependent on another
(d) Forage grasses
- Guinea grass/Panicum maximum
- Stubborn grass/Eleusine indic
- Elephant grass/Pennisetum purpureum
- Giant star grass/Cynodon plectostachyus
- Southern gamba grass/ Andropogon tectorum
- Rhodes grass/Chloris gayana
- Bermuda grass/Bahana grass/Cynodon dactylo
- Spear grass/Imperata cylindrica
- Carpet grass/Axonopus compressu
- Kikuyu grass/Pennisetum clandestinum
- Northern gamba grass/Andropogon gayana
