Question 2
AIM: To determine the relationship between amount of charge in a motor vehicle battery
and time taken to charge.
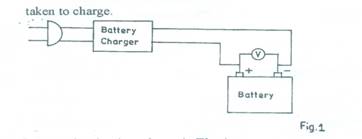
- Connect the circuit as shown in Fig. 1.
- Ask the supervisor to check the circuit connection.
- Set the battery charger to 12V range.
- Plug the battery charger to an a.c. source.
- Read and record the voltage, Vo, across the battery
- Switch on the battery charger and start the stopwatch simultaneously.
- Read and record in Table 3 the voltage V at time t = 10 mins, 20 mins, 30 minsand 40 mins respectively.
- Complete Table 3 by calculating V – Vo.
- Plot a graph of V – Vo (V) on the vertical axis against time (mins) on the horizontal axis.
- Comment on your graph.
- State one application of the experiment.
- State two safety precautions taken in carrying out the experiment.
Table 3
Time (mins) |
Voltage, V (V) |
V – Vo (V) |
10 |
|
|
20 |
|
|
30 |
|
|
40 |
|
|
Observation
The expected responses were:
(e) Voltage across the battery Vo = 10V
Table 3
Time (mins) |
Voltage, V(V) |
V – Vo (V) |
10 |
11.00 |
1.00 |
20 |
11.20 |
1.20 |
30 |
11.30 |
1.30 |
40 |
11.38 |
1.38 |
Voltage V (V) –values ± 0.9 with respect to Voltage, V (V) in Table 2
V – Vo (V) –values with respect to Voltage, V (V) in Table 2
(i) A non-linear graph with appropriate:
- choice of scales.
- pick of points.
- joining of points.
- labelling of axes
(j) Comment on graph
- It is non-linear
- The charging rate decreases with increase in time
(k) Application of experiment
- To determine the quality of a battery
- To determine the charging rate of a battery
(l) Precautions in carrying out the experiment
- Ensure tight connection of the battery terminals
- Ensure the correct polarity of battery
- Ensure good ventilation of the room/area
- Avoid flames/sparks in the area
Questions 2 required candidates to charge a lead-acid battery and measure the terminal voltage of the battery with increase in time of charge. The Chief Examiner reported that only a few candidates attempted question 2 with good responses and deductions.
