|
|
Question 4
|
Study specimens L, M, N, P, Q, R, and S carefully and use them to answer questions 4(a) to 4(d).
- Name two specimens which can be used for the following:
- reproduction;
- protection;
- movement. [6marks]
- Stating observable features in specimens L, M, N, P, Q and R, suggest one reason
each for the answers given in 4 (a) (i), (ii) and (iii) above. [12 marks]
- State:
- two observable similarities;
- two differences between specimens P and R. [4 marks]
- (i) State how observable features of specimen M adapt the specimen to its functions [6 marks]
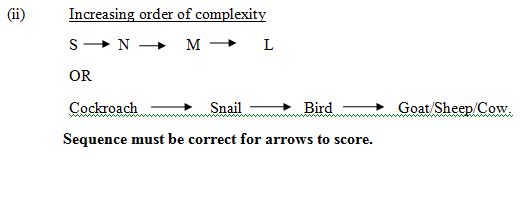
- Arrange specimens L, M, N and S in the increasing orders of complexity of the
organisms to which they belong. [2 marks]
|
| _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ |
|
Majority of the candidates could answer question 4(a) and (b) correctly but could not suggest the reason for stating the observable features stated in 4(b). Many of the candidates could not state the observable similarities and differences and how the observable features adapt specimen M to its function. Many candidates could not also arrange the specimens in their order of complexity.
The expected answers are:
4 (a) (i) Specimens used for reproduction
- Irish potato/Specimen P
- Twig of Hibiscus/Bougainvillea/specimen Q
- Cutting of cassava/Specimen R
(ii) Specimens used for protection
- Skin of a goat/sheep/cow/specimen L
- Quill feather/Specimen M
- Shell of a snail/specimen N
(iii) Specimens used for Movement
- Specimen M/Feather (Quill)
- Specimen S/Hind wing of a cockroach
(b) Observable features with reasons
For reproduction
P/Irish Potato – presence of buds/eye(s); for sprouting to produce/new shoot;
Q/Twig of Hibiscus/Bougainvillea – has buds; for sprouting;
R/Cutting of cassava – has buds; for sprouting.
For protection
L/Skin of a goat – presence of hairs/sheet-like structure to protect the body against mechanical injury;
M/Feather – broad and smooth to cover body and prevent wetting/provides insulation;
N/Shell – hard/calcareous nature to protect soft body of snail.
For movement
M/Feather –those of wings and tail are flat and air-tight for flight;
S/Hind wing of cockroach- light and flexible for flight.
(c) (i) Similarity between specimen P and R
- Both specimens have buds for reproduction;
- both are stems;
- both have lenticels.
(ii) Differences between specimen P and R
- Buds of Irish potato/Specimen P buried in tuber while buds in cassava/Specimen R protrude from the stem;
- buds of Irish potato/Specimen P are covered with scale leaves while the buds in cassava/Specimen R are not covered;
- Irish potato/Specimen P stores food while cassava/Specimen R does not store food.
(d) (i) Adaptation of specimen M to its function
- Vane is stiff; to enable it withstand air pressure during flight;
- vane is broad; to provide a large surface area for air lift;
- vane is made up of barbs interlocked by barbules; providing air tight surface for flight;
- the quill is light and hollow; for buoyancy;
- it is water proof; to prevent birds from getting wet.
|
|
|
|



