Question 3
- A sample of garden soil was placed in a measuring cylinder, enough water was added to it. It was shaken and allowed to settle for 30 minutes. Draw a diagram 6cm-8cm long to show the various layers formed and label fully. [7 marks]
- State four reasons why each of the following soils is not suitable for crop production:
- Clayey;
- Sandy. [8 marks]
- (i) List two examples of refuse. [2 marks]
(ii) State three ways in which refuse is disposed of in the community. [3 marks]
Observation
The diagram of soil profile showing different layers of garden soil was poorly drawn by majority of the candidates. Many candidates drew without the appropriate ways of labeling; spelling errors and no indication of the soil layers. Many candidates mistook sewage for refuse and hence could not give examples.
The expected answers are:
3 (a) Diagram showing different layers of garden soil
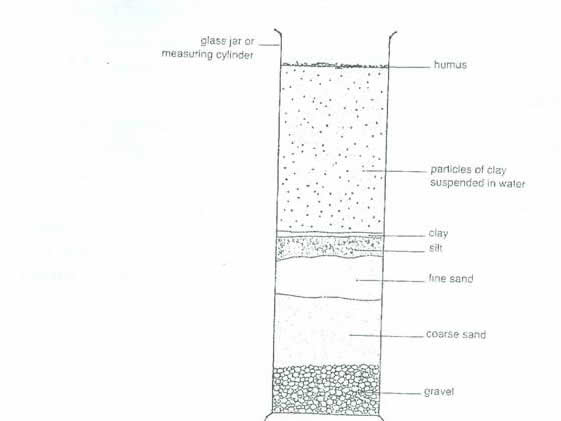
Title (T) x1
Quality (Q)
Size (Sz) (6-8cm) x1
Clarity of lines (CL) x1
Neatness of labels (NL) x1
Details (D)
At least 3 layers shown (SL) x1
Labels (L)
Measuring cylinder; humus/organic matter; clay; silt; fine sand; coarse sand; gravel; water with clay in suspension and mineral salts in solution.
NOTE: Spellings of labels must be correct to score.
(b) Reasons why clayey soil and sandy soil are not suitable for crop production
- Clayey Soil
- Small soil particles; lead to less air space/high water retention/low water drainage; soil becomes water logged easily;
- small amount of oxygen supports few nitrifying bacteria/low in nitrates;
- has few organisms/little humus/low soil nutrients;
- heavy and sticky makes it difficult to cultivate;
- very hard when dry which makes it difficult for plant growth.
- Sandy Soil
- Large/coarse soil particles create more air spaces/it is porous;
- low water retention/high water drainage which makes minerals easily washed out/leached;
- small amount of water makes soil dry therefore plants and animals/organisms find it hard/difficult to get water;
- Soil is light and is easily blown away/eroded.
(c) (i) Examples of refuse
Waste papers; food remnants/domestic waste; cans; plant materials/cobs of maize; yam; cassava; plantain/banana peels; plastic wastes and containers and any other correct example.
(ii) Methods of disposal
Burning/incineration; controlled dumping; recycling/biodegradation; burying.
