QUESTION 2
Study specimens F, G, and H and answer questions 2(a) to 2(f)
- Name the Class to which each of specimens F and G belong. [2 marks]
- State one reason each for the answers in 2(a). [2 marks]
- Name the root system of each of specimens F and G. [2 marks]
- (i) Detach one complete leaf from specimen F and make a drawing, 8 cm to 10 cm long of the leaf and label fully. [8 marks]
(ii) State one function each of three of the labelled parts of the drawing in 2(d)(i).
[3 marks]
- State three ways by which specimen F is of economic importance. [3 marks]
- (i) Describe briefly four observable features of specimen H. [4 marks]
(ii) State one biological significance of specimen H to the plant from which it was obtained. [1 marks]
.
Many candidates interpreted questions 2(a) to 2(d) wrongly by giving wrong responses. They could not give the correct class of specimens F and G. Many candidates also gave wrong diagrams which led to complete loss of marks. Although many candidates knew the type of root system as required in question 2 (c), many still lost vital marks to poor spellings.
Some candidates could not give the structure and function of the labelled parts of the detached leaf as required in question 2(d). However, poor technical details in the diagrams like wrong titles, incorrect magnification, rough diagrams and labeling led to loss of marks for some candidates.
Many candidates also could not correctly answer functions of labelled parts of specimen F/Panicum sp.
The expected answers include:
(a) Class of specimens F/Panicum sp./Guinea grass and G/Cocoyam/Caladium sp.
F: Monocotyledoneae/ Monocotyledonae /Liliopsida.
G: Monocotyledoneae/ Monocotyledonae /Liliopsida.
(b) Reason for Class of specimens F and G
F
- Leaves have parallel venation;
- Leaf sheath present;
- Presence of fibrous root system;
- Narrow leaves/leaves with narrow lamina
- Circular node present.
G
- Presence of fibrous root system/adventitious root;
- Circular node present.
(c) Root systems of specimens F and G
F: Fibrous.
G: Adventitious/contractile/fibrous.
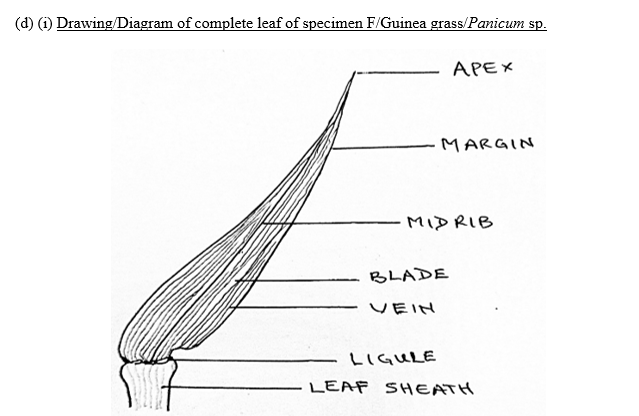
Title (TL) Drawing/Diagram of specimen F/Guinea grass/Panicum sp.
Quality (Q)
Clarity of lines (CL)
Size (SZ) (8 cm to 10 cm)
![]() Neatness of labels (NL) All guidelines ruled -½ mark;
Neatness of labels (NL) All guidelines ruled -½ mark;
All labels horizontal -½ mark
Magnification (MG) (×![]() /×0.1)-0.2
/×0.1)-0.2
Details (D)
Parallel venation shown (PV)
Leaf sheath shown (LS)
Labels (L)
ligule, leaf sheath, lamina/leaf blade, vein, apex, midrib
(ii) Function of three labelled parts of leaf of specimen F/Guinea grass/Panicum sp.
Lamina/leaf blade: Photosynthesizes to make food for the plant/site for gaseous exchange.
Leaf sheath: Supports the lamina/attach the lamina to the stem.
Vein: Contains xylem which conducts water and mineral salts through the leaf/contains phloem to transport manufactured food out of the leaf/gives structural support to leaf/contains supporting tissues.
Leaf ligule: Allows movement of the lamina.
Apex: Allows water drop off the leaf/prevents water retention.
Midrib: Supports the blade.
(e) Economic importance of specimen F/Guinea grass/Panicum sp.
- Used as feed/fodder for cattle;
- Used as fuel;
- For roofing houses/structures;
- For making basket;
- Has medicinal purposes
- Used as rope;
- Used for mulching;
- For generating income.
(f) (i) Observable features of specimen H/corm of cocoyam
- (Vertical) swollen stem;
- Brown in colour;
- Bears concentric rings of nodes;
- Bears tiny brown scale leaves at some points of the nodes;
- Bears tiny axillary bud at some points of the nodes;
- Bears tiny, broad terminal buds;
- Surrounded with relatively large-scale leaves;
- Presence of long adventitious roots.
(ii) Biological significance of specimen H/corm of cocoyam to the plant from which it was
obtained
Vegetative propagation/storage of food/for anchorage.
