Question 3
- (a) (i) Describe briefly how the iodoform test can be used to distinguish between 1- butanol and 2-butanol.
(ii) State any observations made in the test. [5 marks]
(b) Explain briefly each of the following terms:
(i) activation energy;
(ii) ineffective collision.
[6 marks](c) (i) Explain briefly the abnormal behavior of NH3, H2O and HF when
compared with other hydrides.
(ii) Give two examples of the abnormal behavior explained in 3(c)(i).
(d) Study the following reaction scheme and use it to answer the following questions.
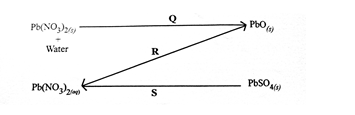
- Describe a suitable procedure for carrying out each of the reactions Q, R and S in the laboratory.
- State the gases produced in addition to PbO in reaction Q.
- State the colour of:
I PbO;
II Pb(NO3)2;
III PbSO4.
- Name one substance that could be used to convert PbO to Pb. [10 marks]
Observation
Majority of the candidates avoided this question.
In part (a), majority of the candidates could not describe how the iodoform test can be used to distinguish between 1-butanol and 2-butanol.
In part (b), majority of the candidates could not explain activation energy and ineffective collision.
In part (c), majority of the candidates could not explain the abnormal behavior of NH3, H2O and HF when compared with other hydrides.
In part (d), majority of the candidates did not attempt this question and those that did could not describe a suitable procedure for carrying out reactions Q, R and S in the laboratory.
The expected answers include:
(a) (i) Add iodine solution / I2 dissolved in KI solution and NaOH solution. Warm the mixture
(ii) 2 – butanol will form yellow precipitate while 1 – butanol will give no reaction
(b) (i) Activation energy is the minimum energy that reactant particles must possess for a reaction to occur
(ii) An ineffective collision is one in which the reacting / colliding particles lack sufficient energy and proper orientation to bring about a chemical
change
(c) (i) This is attributed to hydrogen bonding in the compounds, due to high electronegativity of nitrogen, oxygen and fluorine.
(ii) - high boiling point
- high solubility
(d) (i) Q - is by heating
R - is by adding dilute HNO3 to PbO and warm
S - by adding dilute HNO3
(ii) Gases produced are NO2 and O2 / nitrogen (IV) oxide and oxygen.
(iii) I - PbO - yellowish / brown / orange / red
II - Pb(NO3)2 - white
III - PbSO4 - white
(iv) Carbon / hydrogen gas
