The question was not popular among the candidates and the performance was fair.
In(a)(i), candidates correctly responded to I and II as follows:
I - pressure/volume of vessel
temperature
II - Catalyst
Catalyst affects both forward and backward reactions equally
In (a) (ii], most candidates gave the effect on the equilibrium position instead of the effect
on the equilibrium concentration of Cl2• They therefore lost the marks. The required
answers for I - III were as follows:
(a) (ii) I - Equilibrium concentration of Cl2 decreases.
Increase in pressure shifts equilibrium position to the right where there is
lower number of moles of species.
II - Equilibrium concentration of Clz increases
Increase in temperature shifts equilibrium to the left where the reaction is
endothermic.
III - Equilibrium concentration of Cl2 decreases
Increase in concentration of PCl3 (thereby decreasing the
concentration of Cl2)
In (b)(i), most candidates could not explain that when a standard hydrogen electrode is
connected to a standard copper half cell, the voltmeter reads an emf of O.34V and that the
positive sign indicates the flow of electrons from the hydrogen electrode to the copper
electrode in the external circuit.
In (b) (ii) I - IV, candidates showed shallow knowledge of electrochemistry and hence, lost
most marks for the question. The expected answers from candidates were:
(iii) At Anode
Zn(s) ----+ Zn2+(aq) + 2e-
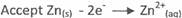
At Cathode
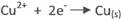
II Anode - oxidation
Cathode reduction
III Zn(s) + Cu2+ (aq) → Zn2+ (aq) + CU(s)
(iv) EO cell = EOreduction - EO oxidation
= 0.34V - (- 0.76V)
= 1.10V
Alternative method
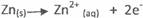 + 0.76V
+ 0.76V
Cu2+ 2e- → Cu(s) + 0.34V
e.m.f. = +0.76 + 0.34
=1.10 V
In part (c), candidates correctly named one chemical industry, gave three factors that
should be considered when sitting a chemical industry and stated two effects of a
chemical industry on the community in which it is sited in (i) - (iii) as follows:
(i) Named chemical industry
e.g Textile
Tannery
Brewery
Bottling Company
Soaps and detergents
Infant formula/Baby food
Food seasoning.
(ii) - nearness to raw material source/feedstock
- nearness to market
- labour supply
- transportation
- nearness to power supply
- government policy
- away from residential areas.
(ii) - improvement in the standard of living of people
- employment opportunities
- development in that community
- pollution (air, land water etc)
.



