This question was attempted by majority of the candidates and the performance was fair.
In (a)(i)(ii) and (iii) most candidates correctly define standard electrode potential, state factors that affect standard electrode potential and gave uses of the values of standard potential. However, some candidates could not properly define standard electrode potential.
In (a)(iv) most candidates could not draw and label correctly electrochemical cell.
In (b) (ii) and (III) only a few candidates could define oxidation in terms of electron transfer. Also majority of the candidates could not balance redox reaction.
In (c) most candidates correctly classified oxides as basic, amphoteric, acidic or neutral.
In (d) most candidates could not correctly define hydrogen bonding.
The expected answers were:
(a) (i) Is a measure of the tendency of an element to form ions in solution relative to
the tendency of hydrogen atoms to form ions in solution at standard conditions
(at 298k and 1 atm. pressure and 1 molar concentration)
(ii) Condition, temperature, pressure.
(iii) - To predict the direction/ feasibility of a chemical reaction.
- To calculate the e. m. f. of a cell.
- To predict the standard potential of unknown elements
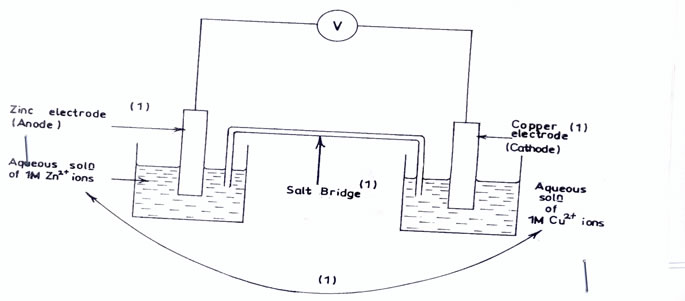
(v) Emf = Eo (Right) - Eo ( left)
+ 0 .34V – (- 0. 76V)
= + 1. 10V
(b) (i) I . Oxidation - a process of election loss.
II. Oxidation agent – Is an electron acceptor.
(ii) Separate into half reactions
2I- ® I2 + 2e
5e+ 8H++ MnO4- ® Mn2+ + 4H2O
Balancing 10I- ® 5I2 x 10e
10e+ 16H+ + 2MnO4- ® 2Mn2+ + 8H2O
10I- +16H+ + 2MnO4- ® 5I2 +2Mn2+ + 8H2O
(c) (i) Neutral
(ii) Acidic
(iii) Amphotenic
(iv) Basic
(d) Hydrogen bonding is an intermolecular force between molecules in which hydrogen is
attached to a very electronegative atom which has a small size e.g N, O, F



