Question 4
(a) With the aid of diagrams, distinguish between change in quantity supplied and change in supply.
(b) Explain any four factors that influence the supply of a commodity.
Observation
This question was very popular among candidates. Candidates were required to distinguish between change in quantity supplied and change in supply using diagrams in the (a) part and to explain four factors that influence the supply of a commodity. The performance of candidates was slightly above average as some candidates mistook change in supply for change in quantity supplied and could not adequately expatiate on their points in the (b) part of the question. Candidates were expected to answer thus to score maximum marks:
- A change in quantity supplied is caused by a change in price while change in supply is caused by changes in all factors influencing supply except the price of the commodity.
Change in supply involves a shift in supply curve while change in quantity supplied involves movement along the same supply curve;
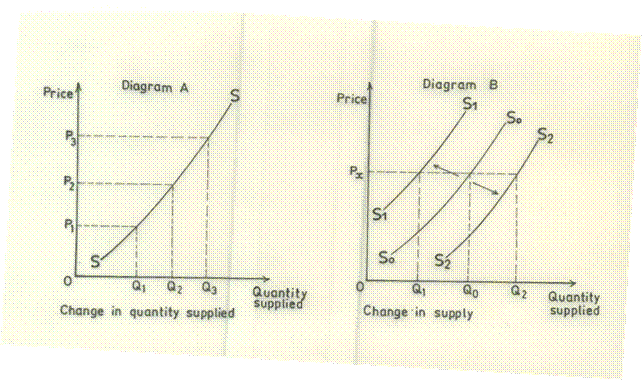
- from diagram A, an increase in price from OP1 to OP2 led to an increase in quantity supplied from OQ1 to OQ2 .
from diagram B, a favourable change in factors affecting supply led to a rightward shift of the supply curve from S0S0 to S2S2 leading to an increase in supply from OQ0 to OQ2 while price remains unchanged at OPx
Note: For Blind Candidates only.
4. (a) (i) A change in quantity supplied is caused by a change in price while change in supply is caused by changes in all factors influencing supply except the price of the commodity.
Change in supply involves a shift in supply curve while change in quantity supplied involves movement along the same supply curve.
(ii) A change in quantity demanded is caused by a change in price while change in demand is caused by changes in all factors influencing demand except the price of the commodity.
Change in demand involves a bodily shift in demand curve while change in quantity demanded involves movement along the same demand curve.
4. (b) (i) Price of the commodity: At higher prices more of a commodity are supplied than at lower prices.
(ii) The prices of related commodities: Changes in the prices of related commodities may cause a producer to shift resources into the production of the commodity whose price have increased.
(iii) Cost of production: A change in the cost of factor inputs will cause a change in supply.
(iv) Weather Conditions: A favourable weather condition will lead to an increase in supply e.g agricultural products and vice versa.
(v) Government taxation: Changes in government tax policies may cause changes in supply.
(vi) Level of technology: Improvement in the level of technology may cause an increase in supply.
(vii) Government policies on subsidies: Introduction or removal of subsidies may affect cost of production which may cause supply to increase or decrease.
(viii) Cost of storage: This may cause supply to increase if low and supply to decrease if high.
(ix) Expectation of future changes in price: If price is expected to rise, suppliers may reduce supply. If price is expected to fall, supply will be increased.
(x) Number of producers: If the number is high, supply will increase and vice versa.
(xi) The goal of the producer: If it is to make maximum profit, supply is increased and vice versa.
