Question 8
(a) (i) State the reason why simple harmonic motion is periodic.
(ii) State two factors that affect the period of oscillation of a simple pendulum.
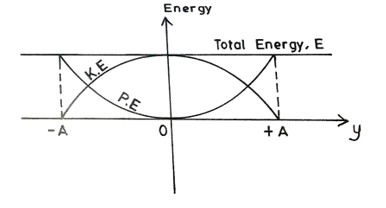
(iii) Sketch a graph of the total mechanical energy, E, against displacement, y, for the motion of a simple pendulum from one extreme position to the other.
(b) The diagram below illustrates an oscillatory pendulum.
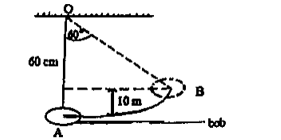
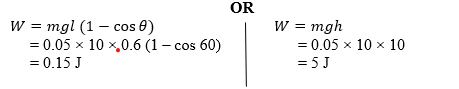
Calculate the work done in raising the pendulum to point B, if the mass of the bob is 50g.
[g = 10 ms-2]
- A spiral spring of spring constant, k, and natural length, l, has a scale pan of mass 0.04kg hanging on its lower end while the upper end is firmly fixed to a support. When an object of mass 0.20kg is placed on the scale pan, the length of the spring becomes 0.055m and when the object is replaced with another object of mass 0.28kg, the length of the spring becomes 0.065 m. Calculate the values of k and l.
[g = 10 ms-2]
Observation
In question 8a, a significant number of candidates were able to aptly justify why Simple Harmonic Motion is periodic.
However, in question 8a(iii), most candidates were unable to obtain the maximum mark possible due to their inability to sketch the graph of the total mechanical energy, E, against displacement, y, for the motion of a simple pendulum.
In question 8b, most candidates did not perform well due to incorrect substitution.
Finally, in question 8c, the majority of candidates failed to answer correctly because they did not take into account the weight of the scale pan.
EXPECTED RESPONSES:
(a) (i) Reason why Simple Harmonic Motion is periodic
- It is a motion that continuously repeats itself (in a specific pattern).
- Due to the balance between the restoring force and the inertial force/weight.
(ii) Factors that affect the period of oscillation of a simple pendulum
- Length (of the pendulum)
- Acceleration of free fall/ acceleration due to gravity
(iii) Sketch of E against y
A6
(b) Calculation of work done
B3
(c) Calculations of values of l and k

