Question 3.
- State three differences between:
- primary cells and secondary cells;
- direct current and alternating current.
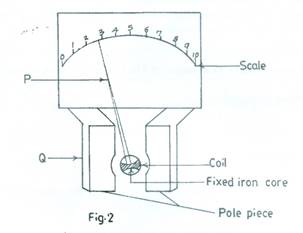
- Fig. 2 is the diagram of a metering coil ammeter reading in milliameter range.
- Name the parts labelled P and Q;
- State the reading displayed by the instrument.
- if the reading of the instrument in Fig. 2 was recorded when it was connected to circuit of 1 kΩ resistance, calculate the:
- Voltage drop in the circuit;
- Power dissipated by the circuit.
Observation
The expected answers were:
The expected responses were:
(a) (i) Differences between primary cells and secondary cells
Primary cells |
Secondary cells |
They are not rechargeable |
They are rechargeable |
They are usually light in weight |
They are usually heavy |
Electrolytes are usually in solid/paste form |
Electrolytes are usually in liquid form |
They are usually single celled |
They are usually multi-celled |
They have shorter shelf life |
They have longer shelf life |
They are cheaper |
They are more expensive |
(ii) Differences between direct current and alternating current
Direct Current |
Alternating current |
Its output is a straight line |
Has a sinusoidal/non-linear waveform |
Has no frequencyor zero frequency |
Has frequency/ has non-zero frequency |
Total electrical energy is effective energy. |
Total electrical energy is not effective energy. |
Non- reversible polarity |
Reversible polarity |
Its source is battery/solar cells |
Its source is the mains/generator |
Current flows in one direction |
Current direction is reversible. |
(b) (i) P – pointer
Q – permanent magnet
(ii) Reading = 2.7 – 2.9 mA.
(c) (i) ![]()
![]() (to
(to ![]() )
)
![]()
(ii) ![]() OR P = V2/R OR
OR P = V2/R OR ![]()
![]() OR
OR ![]()
![]() 7.29mW
7.29mW
![]()
It was reported that majority of the candidates that attempted Question 3 responded very well. Only a few candidates could not read the ammeter scale appropriately.
