This question was poorly attempted by the candidates. In 3(a)(i – ii), majority of the candidates could not define the terms hay and silage. In 3b(i – iii), though, most of the candidates were able to name the types of pasture but majority of them could neither state the advantages of establishing a grass-legume pasture nor state the advantages of rational grazing.
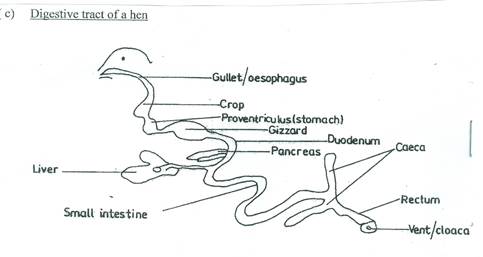
Also, most of the candidates could not draw and label the digestive tract of a hen as required in 3(c).
The expected answers include:
(3) (a) Definition of the terms hay and silage
(i) Hay
This is a cut and dried forage (stored) for feeding farm animals
Silage
This is a cut and fermented forage in an anaerobic condition
for feeding farm animals
(b) (ii) Advantages of establishing a grass-legume pasture
- It suppresses weed
- Improves nutritional quality of the forage/balanced diet
- Legumes fertilize the soil for grass to grow/nitrogen fixation
- Optimal usage of the land
- It enhances proliferation of soil fauna and flora leading to
improved soil structure, texture and aeration
- Reduces evapotranspiration or water loss
- It prevents erosion
- Legume trails on the grass for more production/High yield/
improved income
- Legume serves as source of protein for the livestock
- It is more acceptable to ruminants
- It reduces leaching
(iii) Advantages of rotational grazing
- Prevents overgrazing
- Allows for the regeneration of grazed forage
- It controls parasites/diseases/pests
- Promotes efficient utilisation of pasture
- Reduces soil compaction/maintenance of soil structure
 |



