Question 6
(a) Draw a marketing channel for table eggs. (7 marks)
(b) Give three ways of stabilizing the process of agricultural produce in West Africa. (3 marks)
(c) List two ways each by which land;
(i) appreciates;
(ii) depreciates. (4 marks)
(d) State two deficiency symptoms of each of the following nutrients in crops;
(i) potassium;
(ii) phosphorus. (4 marks)
Observation
Question 6 was attempted by few candidates and responses were poor. Many candidates could not draw the marketing channel for table eggs but were mentioning the marketing agents only without linking their relationship. Furthermore, candidates were unable to state ways by which land appreciates and depreciates.
The expected answers include:
6. (a) Marketing channel for table eggs
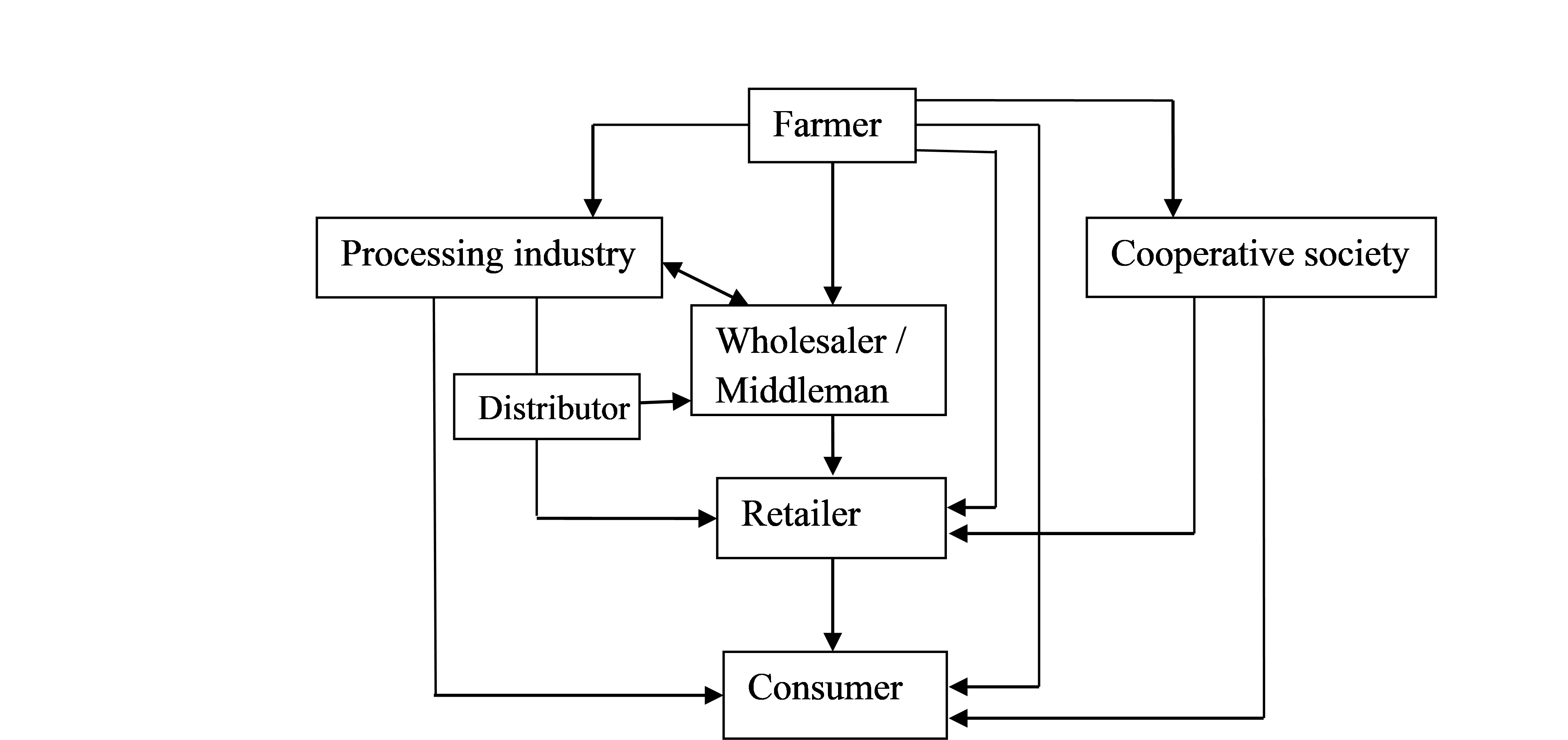
(b) Ways of stabilizing the prices of agricultural produce in West Africa
- Buffer stock / storage of surplus output
- Price control (price ceiling and price floor)
- Provision of subsidies
- Price support by government
- Establishment of marketing / commodity boards
- Intervention buying and selling of produce
- Allocation of production quota to farmers
- Regulation of import/export of agricultural produce
- Introduction of standardized / uniform weights and measuring devices
- Formation of farmers’ cooperatives
(c) Ways by which land appreciates and depreciates
(i) Appreciate
- Fallowing - Cover cropping
- Irrigation - Weeding
- Good access roads - Drainage
- Manuring /fertilizer application - Afforestation
- Appropriate tillage practice
- Crop rotation
(ii) Depreciate
- Erosion - Weed infestation
- Overgrazing - Mining
- Indiscriminate bush burning - Deforestation
- Desertification
- Infestation by pests and diseases on planted crops
- Dumping of toxic materials/soil pollution
- Continuous cultivation without application of manure or fertilizer
(d) Deficiency symptoms of nutrients in crops
(i) Potassium
- Leaves appear dry and scorched at the edges
- Surfaces of leaves appear irregular and may be chlorotic - Poor tuber formation
- In cereals, grains are not properly developed and cobs are not ‘filled’
- Delayed maturity
(ii) Phosphorus
- Premature fruit drop
- Poor fruit and pod formation
- Weak stem development which makes plants susceptible to lodging - Poor root formation
- Mottling of leaves
- Purple/violet colouration on leaves
