Question 1
(1) (a) Identify the type of fuel pump shown below:
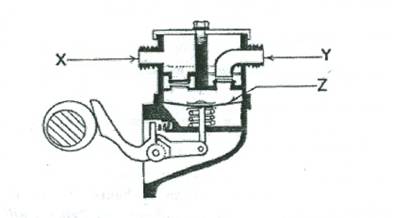
(b) Name the parts labeled X, Y and Z.
(c) Describe:
(d) State one effect of a punctured diaphragm.
Observation
This question attracted most of the candidates. Their inability to identify the fuel pump shown affected their performance. However they faired well in part (d) of the question. The required response to other parts of the question are:
Y is outlet or delivery port;
Z is diaphragm.
(c) (i) Intake Stroke – An eccentric lobe on the engine camshaft actuates the operating arm of the pump which moves the diaphragm up and down. On the downward movement of the diaphragm, a depression is created in the upper pumping chamber. Petrol, under atmospheric pressure flows into the chamber. As the eccentric rotates, it allows the return spring to force the diaphragm upwards. As it does so, the inlet valve closes, the outlet valve opens, and petrol is forced into the carburettor float chamber.
(ii) Idling Stroke – When the float chamber is filled to its correct level, delivery is stopped by the action of the float operated needle valve. Diaphragm and link arm are held in their down position; the rocker arm follows the eccentric, but its face cannot contact the face of the link arm. The diaphragm cannot therefore move, and the pump idles until such time as the float needle valve is opened again.
