This question was not a popular question among the candidates and the candidates who attempted it did not perform well. Most candidates drew very poor diagrams of the heart with woolly and broken lines and loss of details. They did not conform to size specifications and did not give titles to their diagram which resulted in loss of marks. More than half of the candidates could not describe pulmonary circulation, a lot of them merely defined it and so lost a lot of marks. Most candidates could also not state four differences between pulmonary and systemic circulation
Expected answers include:
Pulmonary Circulation
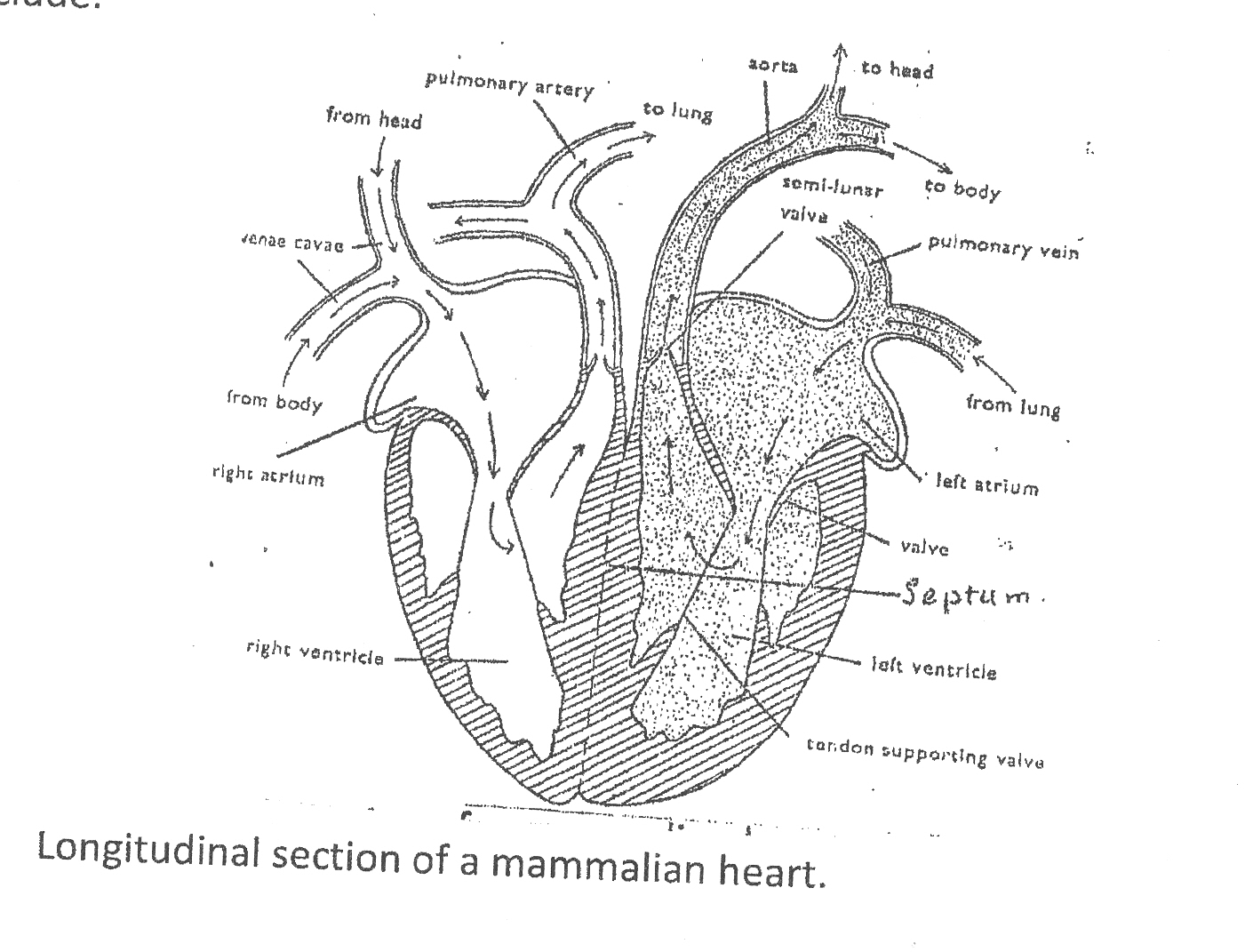
Longitudinal section of a mammalian heart.
Pulmonary Circulation
Mammalian blood – flow from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart is known as pulmonary circulation;
deoxygenated blood from the body is brought to the right atrium/auricle through the venae cavae/superior and inferior vena cavae/posterior and anterior vena cavae; When the right auricle/atrium is filled with blood; it contracts; the tricuspid valve; opens to allow blood flow into the right ventricle;
the tricuspid valve closes; and the right ventricle contracts; forcing blood through the pulmonary artery to the lungs; for oxygenation; oxygenated blood then flows to the left atrium/auricle; through the pulmonary veins.
Differences between pulmonary and systemic circulation
Pulmonary |
Systemic |
- The circulation is between the heart
and the lungs;
- Oxygenated blood is carried to the
heart;
- Pulmonary vein carries oxygenated
blood;
- Pulmonary artery carries ;
de-oxygenated blood;
- Blood is pumped at low pressure;
- Few blood vessels are involved. |
The circulation is between the heart and
the rest of the body;
De-oxygenated blood is carried to the
heart;
Veins carry de-oxygenated blood;
Arteries carry oxygenated blood;
Blood is pumped at high pressure;
Many blood vessels are involved. |



