Question 1
1. (a)
(i) Cut a piece of specimen A, place it on the white tile. Add a few drops of iodine solution. Record the observation and result in a tabular form. [3 marks]
(ii) Squeeze a few drops of specimen E on another clean white tile provided, add a few drops of iodine solution. Record the observation and result in a tabular form. [3 marks]
(b) (i) State two observable differences between specimens A and B. [2 marks]
(ii) Suggest two factors that are likely to be responsible for the state of specimen B. [2 marks]
(iii) With the aid of a hand lens/magnifying lens, observe specimen B and name an organism likely to be growing on it. [1 mark]
(iv)State the mode of feeding of the organism growing on specimen B. [1 mark]
(c) (i) Make a drawing, 6cm-8cm long of specimen C and label fully. [10 marks]
(ii) State one function each of any three parts labelled. [3 marks]
Observation
In Question 1(a)(i), having carried out the food test as directed, candidates lost marks in writing down the observations and results. Majority of candidates only wrote down the colour observed. While in 1(a)(ii), some candidates failed to write down the specimen and colour change but instead wrote ‘no reaction’. Some candidates also wrote carbohydrate instead of starch.
Majority of candidates could answer 1(b) as expected but lost some marks to the spelling of technical terms. Some candidates could not state the factors responsible for the state of specimen B (bread with mould).
In Question 1(c)(i), most of the diagrams were not drawn to specification and no title was given to the diagram. Also, many candidates failed to write the magnification of the diagram drawn.
In 1(c)(ii), candidates were able to state the function of the labelled parts.
The expected answers are:
- (a) Food Test
|
Observation |
Result |
i |
Specimen A/bread/;it turns blue-black
|
Starch present |
ii |
Specimen E/Orange juice turns brownish/yellowish |
Starch absent |
6 x 1 [6marks]
(b) (i) Observable differences between specimens A and B
- Specimen A is white/cream in colour while Specimen B is dark brown/ black/ orange in colour;
- Specimen A is soft in texture while Specimen B is hard in texture;
- Absence of mould/Rhizopus/Mucor in Specimen A, while in Specimen B, there is presence of mold/mould, fungus/fungi/Rhizopus/Mucor.
- Specimen A is fresh, while Specimen B is stale/decaying. Any 2 x 1 [2 marks]
(ii) Factors responsible for the state of specimen B
- Moisture/water/humid air/humidity;
- Warmth/temperature;
- Spores of fungus/fungi;
- Time. Any 2 x 1 [2 marks]
(iii) Name of organism
Mold/mould/fungus/fungi/Rhizopus/Mucor. Any 1 x 1 [1 mark]
(iv) Mode of feeding
Saprophytic 1 x 1 [1 mark]
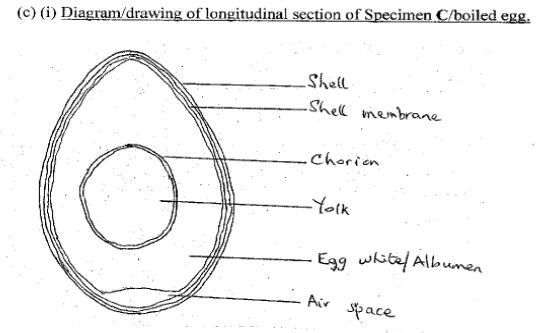
Title (TL)
Quality (Q)
Clarity of lines (CL)
Neatness of labels (NL)
Correct Size (Sz) 6cm-8cm
Magnification (Mg) (x1 - 1½)
Details (D)
Yolk centrally located (YC)
Cut surface shown in double lines (CS)
Big albumen shown (BA)
Labels (L)
Shell; egg white/albumen; yolk; air space, shell membrane, chorion.
(ii) Function of labelled parts
- - Shell: Protection/aeration/shape/gaseous exchange;
- - Shell membrane allows gaseous exchange;
- - Albumen: Supplies protein;
- - Yolk: Provides food for embryonic growth/embryo;
- - Air space: allows exchange of gases;
- - Chorion protects the embryo/yolk sac.
