Question 2
- Name the location of each of specimens H, K and M in the body of a mammal. [3 marks]
Study specimens H, K, L and Mcarefully and use them to answer
questions 2(a) to 2(e).
(b) (i) Name the fluid in specimen L . [1 mark]
(ii) State two functions of the fluid named in 2(b)(i). [2 marks]
(iii) Which of the other specimens is specimen L associated with? [1 mark]
(c) (i) State two observable differences between specimens H and K. [2 marks]
(ii) State two observable features of specimen K that adapt it to its function.
[4 marks]
(d) State one biological importance each of specimens K and M. [2 marks]
(e) Make a drawing, 8cm-10cm long of specimen M and label fully. [10 marks]
Observation
Many candidates could not name the location of specimens H (fresh liver), K (fresh lung) and M (fresh kidney) in the body of a mammal correctly. Some of the few that got the correct location missed the mark to poor spellings.
Some candidates could not name the fluid in specimen L (gall bladder) but state the functions of the bile. Majority of the candidates could state that specimen L (gall bladder) is associated with specimen H (fresh liver).
Only a few candidates were able to state the observable differences between specimens H (fresh liver) and K (fresh lung). A few candidates were able to state the features that adapt specimen K (fresh lung) to its function.
Question 2(d) was well answered.0
Many candidates did not draw specimen M (longitudinal section of kidney) to specifications; some diagrams were not bean-shaped; the three regions not shown; and the magnification of the drawing was not written.
The expected answers include:
- (a) Location of specimens H, K and M in the body of a mammal
Specimen H/Liver: Below the diaphragm/ upper part of abdominal cavity/abdomen;
Specimen K/Lung: Thoracic cavity/chest/thorax/thoracic region;
Specimen M/Kidney: located at the dorsal wall of the abdominal cavity/abdomen.
(b) (i) Fluid in specimen L
Bile.
(ii) Functions of the fluid in specimen L
- - It emulsifies fats (and oils into fat droplets);
- - The inorganic salts in it neutralize the acid in the chyme/bile neutralizes chime;
- - It provides alkaline medium for pancreatic juice to act;
- - It prevents the decay of food in the small intestine.
(iii) Other Specimen that Specimen L is associated with
Specimen H/Liver.
(c) (i) Observable differences between Specimens H/Liver and K/Lung
- - Specimen H/Liver is more solid/thick/turgid while Specimen K/Lung is soft/softer/fluffy;
- - Specimen H/Liver is darker/ dark red in colour while Specimen K/Lung is brighter/red/pink in colour;
- - Specimen H/Liver is smoother on the surface while Specimen K/Lung is folded/convoluted surface.
(ii) Observable features that adapt Specimen K/Lung to its function
- - Moist/wet surface; for dissolving gases/O2/CO2;
- - Thin surface membrane for easy diffusion/exchange of gases;
- - Many blood vessels/highly vascularised/for transportation of gases/dissolved food substances.
NB: Structure and function must correspond to score.
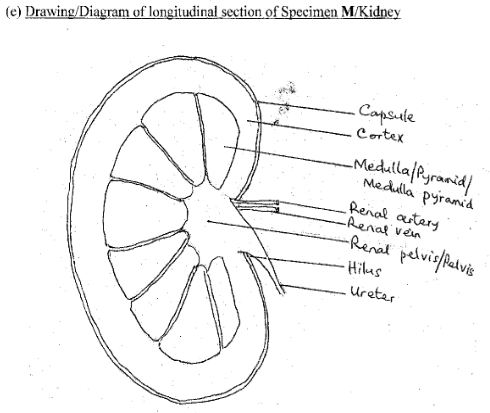
Title (TL)
Quality (Q)
Clarity of lines (CL)
Neatness of labels (NL)
Correct Size (SZ) 8cm-10cm
Magnification (Mg) (x1 - 1½)
Details (D)
Bean shaped kidney (BS)
Three regions shown (TR)
Labels (L)
Cortex; Medulla/Pyramid/Medulla Pyramid; Pelvis/Renal Pelvis; Ureter; Renal artery; Renal vein; Hilus; Capsule.
