Question 1
- The diagram below is an illustration of the longitudinal section of a plant organ.Study it carefully and answer questions 1(a)(i) to (vii).
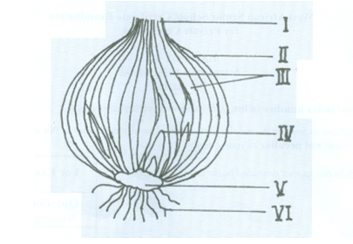
(i) Identify the organ illustrated. [1 mark]
(ii) Name the class to which the plant organ belongs. [1 mark]
(iii) State two reasons for the answer in (a)(ii). [2 marks]
(iv) Name the parts labelled I to VI. [3 marks]
(v) In which of the labelled parts is food stored? [1 mark]
(vi) State one function each of the parts labelled II, III and VI. [3 marks]
- The diagram below is an illustration of a fruit.Study it carefully and answer questions (b)(i) to (b)(viii).
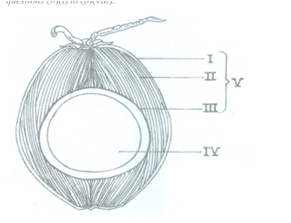
(i) Name the parts labelled I to IV. [2 marks]
(ii) State one function each of the parts labelled I and II. [2 marks]
(iii) Name the type of fruit illustrated. [1 mark]
(iv) State two reasons for the answer in (b)(iii). [2 marks]
(v) Name two examples of plants that have fruit similar to the one illustrated. [2 marks]
(vi) Suggest two agents of dispersal of the fruit. [2 marks]
(vii) State three ways in which the fruit is of importance to humans. [3 marks]
Observation
Some candidates stated the name of the plant illustrated instead of naming the plant organ.
Majority of candidates answered question (a)(ii) poorly, as they could not state the class to which the plant organ belong, and those that could answer it started the answer with a small letter. Some candidates were able to name and state the function of the labelled parts, and state the part that stores food.
Some Candidates could name the parts labelled but could not state the function of the labelled parts.
Some Candidates could name the type of fruit illustrated in (b) (iii) but could not state the reason for the answer properly.
Majority of the candidates were able to answer questions 1(v) to (vii) satisfactorily.
The expected answers are:
1.(a) (i) Identification of Organ
Onion bulb/bulb of onion plant.
(ii) Class of plant organ
Monocotyledoneae
(iii) Reasons for answer in (a) (ii)
- Elongated/ long leaf or leaves;
- Presence of adventitious roots/fibrous roots.
(iv) Names of labelled parts
I- Foliage leaf;
II- Scale leaf/membranous leaf;
III- Fleshy/storage/succulent leaves;
IV- Axillary/lateral bud;
V- Stem;
VI- Adventitious root/fibrous root. ;
(v) Part of plant in which food is stored
Fleshy/storage/succulent leaf/III.
(vi) Functions of parts labelled II, III and VI
II/Scale leaf: For protection of the organ;
III/Fleshy/storage/succulent leaf: For storage of food;
VI/Adventitious root: Absorption of water/mineral salts; anchorage.
(b) (i) Name of labelled parts
I- Epicarp;
II- Mesocarp;
III- Endocarp;
IV- Seed.
(ii) Functions of parts labelled I and II
I/Epicarp: protection/water proof;
II/Mesocarp: buoyancy/dispersal/protection/float.
(iii) Type of fruit illustrated
Drupe
(iv) Reasons for the answer in (b) (iii)
- Possession of thin epicarp;
- Mesocarp is fibrous;
- Endocarp is stony/hard;
- One-seeded fruit.
(v) Examples of plant
- Mango;
- Oil palm;
- Coconut;
- Fan pan.
(vi) Agents of dispersal
River/Water; man
(vii) Importance of fruit to humans
- Source of income/employment;
- Mesocarp is used for making fire/fuel;
- Mesocarp is used for scrubbing;
- Produces oil for cooking/lubrication/cosmetics;
- Endocarp is used as a container;
- Mesocarp is used for making door mat/foot mat;
- Coconut milk is medicinal;
- Used as food/drinks/coconut rice/confectionaries.
