Question 4
-
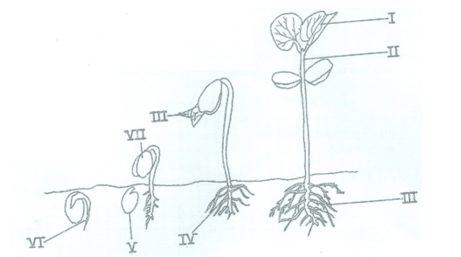
The diagrams below are illustrations of a process in flowering plants. Study the diagrams carefully and answer questions 4(a) to (d).
-
(i) Name the parts labelled I to VIII. [4 marks]
(ii) State one function each of the parts labelled I and II, IV, V, VI and VII. [6 marks]
-
(i) Name the type of germination illustrated. [1 mark]
(ii) Name three examples of seeds that can give rise to the type of germination illustrated. [3 marks]
(iii)Explain briefly the process of germination illustrated by the organism. [7 marks]
(i) Explain how the part labelled VII is carried above the soil level. [3 marks]
(ii) Which labelled part in the diagram stores food? [1 mark]
(iii) Suggest the food substance likely to be present in the part named in (c)(ii) above. [1 mark]
- State three observable differences between organisms D and G.
- (d) State four conditions necessary for the process illustrated by the diagrams to take place. [4 marks]
Observation
Some candidates could not name all the parts labelled in question 4 but they could state the function of some of the parts that were named. The type of germination illustrated could not be named by most candidates although most of them could name other examples of seeds that give rise to the type of germination illustrated.
Many candidates could not explain the process of germination of the illustrated seed in the diagram. Majority of the candidates could not also explain how the part labelled VII is carried above the soil while stating the proper names of structures.
Candidates could answer (c)(ii), (iii) and (d) partially.
The expected answers are:
(a)(i) Name of labelled parts
I- Leaf veins;
II- Epicotyl;
III- Lateral root/secondary root;
IV- Tap root/primary root/main root;
testa/seed coat;
VI- radicle;
VII- cotyledon;
VIII- foliage leaf/plumule.
(ii)Functions of parts labelled I, II, IV, V, VI and VII
I/ Leaf veins: conduct water/mineral salts/manufactured food;
II/Epicotyl: supports the leaves; carry water/food throughout the plant;
IV/Tap root/primary root/main root: anchors plants firmly to the soil/absorbs water/mineral salts;
V/Testa/seed coat: protects the seed (from fungi/bacteria/spoilage organisms/insects);
VI/Radicle: grows downwards to form the root system;
VII/Cotyledon: stores food/ source of energy for germination.
(b) (i) Type of germination illustrated
Epigeal germination.
(ii) Examples of seeds that give rise to the type of germination illustrated
- Mango seed;
- Orange seed;
- Tomato seed;
- Bean seed;
- Castor oil seed;
- Crotalaria seed;
- Cashew nut;
- Date palm seed;
- Groundnut seed;
- Flamboyant seed
- Any correctly named example.
(iii) Process of epigeal germination
- The testa splits;
- The radicle emerges;
- The radicle grows downward;
- Lateral roots develop/appear;
- Hypocotyl elongates;
- Pulling the cotyledons above the ground;;
- The testa is left in the soil;
- The hypocotyl is bent over;
- Carrying the cotyledons still closed together;
- To protect the plumule;
- The hypocotyl straightens;
- The cotyledons split/open;
- Foliage leaves emerge;
- Epicotyl grows out;
- Showing the apical bud;
- Foliage leaves open.
(c)(i) How the part labelled VII is carried above the soil
- The bent-over/hook-like hypocotyl;
- Straightens out/elongates;
- carrying the cotyledons upward.
(ii) Part that stores food Cotyledon/VII
(iii) Food substance storedStarch/carbohydrate/protein/oil
(d) Conditions necessary for the process illustrated in the diagrams
- Viable seed;
- Moisture/water;
- Air/oxygen;
- Warmth/suitable temperature;
- Light/sunlight.
