Question 4
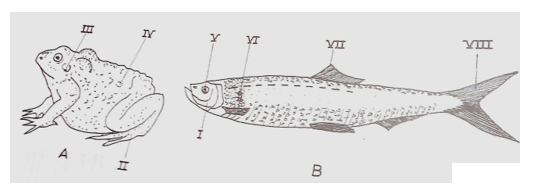
- Name the parts labelled I to VIII. [4 marks]
-
(i) State five observable differences between the vertebrates illustrated as A and B.[5 marks]
(ii) State three observable similarities between the vertebrates illustrated as A and B. [3 marks]
(i) Name the classes to which vertebrates A and B belong. [2 marks]
(ii) State three ways by which the vertebrate illustrated as B is adapted for movement in its habitat. [6 marks]
(iii) Suggest the food substance likely to be present in the part named in (c)(ii) above. [1 mark]
(i) State three ways by which the vertebrate illustrated as A defends itself from its predators. [6 marks]
(ii) Suggest two habitats of the vertebrate illustrated as A. [2 marks]
(iii) State two ways by which the vertebrate illustrated as B is of economic importance to humans. [2 marks]
Diagrams A and B are illustrations of two vertebrates. Study them and answer questions 4(a) to (d).
Observation
Candidates were able to identify the labelled parts but had difficulty in enumerating the difference and similarities between A and B. However, candidates could not distinguish between the tail fin and tail of a fish. Candidates were also unable to classify the organisms. The few that classified properly missed marks to poor spelling and not starting the name with capital letter Some were also unable to explain how the fish adapts itself to its movement in water and explain the features the frog uses to defend itself from predators.
The expected answers are:
(a)Name of labelled parts
I- Operculum/gill cover;
II- Hind limb;
III- Eardrum/tympanum;
IV- (Rough/warty) skin;
VI- eye;
VII- scale;
VIII- dorsal fin;
VIII - tail fin/caudal fin. 8 x ½ [4 marks]
(b)
(i)Observable differences between vertebrates A and B
(ii)Similarities between A and B
Presence of
- eyes;
- mouth;
- nostril;
- skin;
- head;
- trunk;
- streamlined body.
(c)
(i) Classes of A and B
A - Amphibia;
B – Osteichthyes.
(ii)Adaptation of B/Fish to movement in its habitat
- Possession of streamlined body; for smooth movement;
- Possession of lateral line; for sensitivity/detection of vibrations/disturbance in water;
- Possession of tail fin/caudal fin; that propels the fish;
- Possession of anal fin; keeps fish upright/prevents rolling/yawing;
- Pectoral/pelvic fin/paired fins; control balancing/braking/steering;
- Possession of large eyes; which give a wide range of vision;
- Possession of backwardly pointing scales; that reduce resistance to movement in water
Note: Structure and function must correspond to score
(b) (i) Ways by which A/frog defends itself from predators
- Presence of poison gland; which secretes poisonous/distasteful substances;
- Presence of strong/longer muscular/powerful hind limbs; for hopping;
- Presence of shorter/stout/muscular forelimbs; for absorbing shock while landing;
- Presence of webbed hind limbs; to swim away from predators in water;
- Presence of bulging eyes; for sharp/wide range of vision;
- Colour of skin; for camouflage
Note: Structure and function must correspond to score.(ii) Habitat of vertebrate A/frog
- Wet/moist/humid/damp place(s)/land
- Under stones/logs;
- Damp grass/vegetation near pond/stream.
Note: Land alone does not score.
(e)Economic importance of B/Fish to humans
- Its oil is used as medicine/contains omega 3 oil;
- It is used as food/source of protein;
- Used as animal feed;
- It is a source of income/employment for fishermen;
- For biological control of mosquito larvae
