Question 3
The diagrams below are illustrations of the lock and key theory of enzyme action. Study them and answer questions 3 (a) to 3 (e).
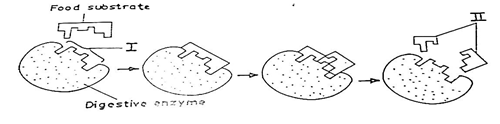
- (a) (i) Name the parts labeled I and II. [2 marks]
(ii) Give three reasons why a small amount of a digestive enzyme is required to catalyze a reaction of a large amount of food substance. [3 marks]
- Complete the table below.
Food substrate |
Enzyme |
Part labeled II |
|
Ptyalin |
|
|
|
Amino acids |
Fats and oil |
|
|
|
Pancreatic amylase |
|
[8 marks]
- (i) Give two reasons why enzymes are specific in action. [2 marks]
(ii) List three factors that affect the activities of digestive enzymes. [3 marks]
(iii) List three uses of enzymes in industries. [3 marks]
- Name the major constituents of enzymes. [1 mark]
- Complete the table below on the effect of varying temperature on digestive enzymes.
Range of temperature |
Effect on digestive enzyme |
Reason for the effect |
5oC - 10oC |
|
|
36oC - 37oC |
|
|
40oC - 45oC |
|
|
95oC - 100oC |
|
|
[8 marks]
Observation
Majority of candidates could not use the knowledge of the characteristics of enzymes to answer the question. They displayed very little knowledge of the topic.
Some candidates could not name the parts labelled I and II, despite food substrate and digestive enzyme were both labelled in the diagram.
Many candidates could not give reasons why a small amount of a digestive enzyme is required to catalyze a reaction of a large amount of food substrate.
Some candidates were able to complete the table on food substrates and the enzyme that catalyze them. While some could not fill the space for Part labelled II.
The major strength of candidates was in stating the uses of enzymes in industries.
Only a few candidates were able to complete the table on the effect of varying temperatures on enzymes.
Majority could not use their knowledge of effect of temperature on enzymes to answer the question.
The expected answers are:
3. (a) (i) Parts labelled
I - Active site;
II - Products.
Note: spellings must be correct to score.
(ii) Reason a small amount of digestive enzymes is required to catalyse a large amount of food substrate
- Digestive enzymes are biological catalysts;
- needed in small amounts to speed up the rate of digestion;
- and they remain chemically unchanged;
- hence the enzyme can be used over and over again.
(b) Process of digestion
Food substrate |
Enzyme |
Part labelled II |
(Cooked) starch |
|
Maltose |
Protein |
Renin/pepsin/trypsin |
|
|
Lipase |
Fatty acids and glycerol/carboxylic |
Starch |
|
Maltose |
(c) (i) Reasons enzymes are specific in action
- Enzymes normally have their active site;
- which has a shape that fits perfectly into a substrate of the same shape;
- an enzyme will not fit into a differently shaped substrate/lock and key.
(ii) Factors that affect the activities of enzymes
- Temperature/heat;
- pH;
- concentration of enzyme;
- concentration of substrate;
- presence of any inhibitors/activators.
(iii) Uses of enzymes in industries
- in brewing/fermentation;
- in biogas production;
- in baking;
- in the production of insulin/renin;
- in textile industries;
- in pharmaceuticals/cosmetics;
- in production of detergents/surfactants;
- in dairy/cheese-making;
- in extracting fruit juice;
- in tanning leather.
(d) Chemical constituents of enzymes
Protein
(e) Effect of varying temperature on digestive enzymes
Range of temperature |
Effect on digestive enzymes |
Reason for the effect |
5oC - 10oC |
Very slow rate of reaction |
Enzyme is inactivated |
36oC - 37oC |
Works best/optimum action |
Activated/optimum temperature range |
40oC - 45oC |
Slow rate of reaction/no action/ |
The enzyme is denatured/enzyme is |
95oC - 100oC |
Enzyme is inactive/no action |
The enzyme is denatured/enzyme is |
