Question 4
. (a) (i) Name a suitable drying agent for the preparation of carbon (IV) oxide
in the laboratory.
(ii) Using one chemical test, distinguish between carbon(II) oxide
and carbon (IV) oxide. [4 marks]
(b) (i) Describe briefly how oxygen and nitrogen could be obtained separately
from air on an industrial scale.
(ii) State how a lighted splint can be used to distinguish between
samples of oxygen and nitrogen. [5 marks]
(c) (i) Give one reason why bauxite is usually preferred as the ore for the
extraction of aluminum.
(ii) List two main impurities usually present in bauxite.
(iii) State the function of sodium hydroxide solution in the extraction
of aluminium from its ore.
(iv) Explain briefly why it is difficult to extract aluminum by chemical
reduction of aluminum oxide.
(v) Write an equation for the reaction of aluminum oxide with aqueous
sodium hydroxide. [7 marks]
(d) (i) The melting and boiling points of sodium chloride are 801o C and
1413oC respectively. Explain briefly why sodium chloride does not
conduct electricity at 25oC but does so between 801oC and 1413oC .
(ii) State the reason why sodium metal is stored under paraffin oil in the
laboratory. [5marks]
(e) (i) State what would be observed when aqueous sodium trioxocabonate
(IV) is added to a solution containing iron (III) ions.
Observation
Majority of the candidates did not respond to this question , and the few that
responded to it did not perform well.
In part (a), majority of the candidates could not name a suitable drying agent for carbon (IV) oxide. Few that got it right, wrote the formula instead of name. However majority of the candidates distinguished correctly between carbon (II) oxide and carbon (IV) oxide.
In part (b), majority of the candidates could not satisfactorily describe how oxygen and nitrogen could be obtained from air on an industrial scale. However, they stated how a glowing splint could be used to distinguish between nitogen and oxygen .
In part (c), majority of the candidates could not list the two main impurities usually present in bauxite. It was reported that they could not state correctly the function of sodium hydroxide solution in the extraction of aluminum from its ore. In addition, they could not write the chemical equation for the reaction between aluminum oxide and aqueous sodium hydroxide.
In part (d), majority of the candidates could not explain why sodium chloride does not conduct electricity at 250C, but stated why sodium metal is stored under paraffin oil in the laboratory.
In part (e), majority of the candidates could not write a balanced equation for the reaction of sodium trioxocarbonate (IV) with solution of iron (III) ions,
The expected answers include:
(a) (i) (concentrated) tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid
(Fused) Calcium chloride
(ii) Pass / bubble each gas into lime water if lime water turns milky then
CO2 is present if no reaction then CO is present
(b) (i) - Atmospheric air is compressed and cooled to liquefy it
- The liquefied air undergoes fractional distillation
- Nitrogen boils out first (at – 196oC) followed by
Oxygen (at – 183oC)
(ii) - Splint burns brighter / continues to burn in oxygen
- Splint is extinguished in nitrogen
(c) (i) - Bauxite is more abundant than any other ore
- Bauxite has less percentage of silicates as impurity
(ii) - Iron (III) oxide
- Trioxosilicates (IV)/silica / sand
(iii) To dissolve the aluminium oxide so that the impurities can be filtered off
(iv) Aluminum is very reactive to be reduced by the common reducing agent
during extraction.
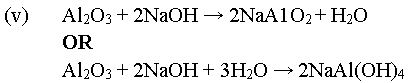
(d) (i) The ions are not free at 25oC since sodium chloride is in the solid state
but between 801oC and 1413oC the ions are free/mobile since it
is now in the molten / liquid state
(ii) Sodium metal is very reactive with air / it is easily oxidised
in air /tarnishes easily
(e) (i) Brown precipitate / reddish brown / orange solid formed.
