Question 2
(a) How many atoms are there in 10.0 g of CaCO3?
[C = 12.0; O = 16.0; Ca = 40.0; Avogadro’s constant = 6.02 x 1023]
[5 marks]
(b)
(i) Write a balanced chemical equation to show the acidic nature of each of the
following compounds when reacted with sodium:
(I) C2H2;
(II) C2H5OH.
(ii) name the major product in each of the reactions in 2(b)(i).
[6 marks]
(c) Consider the following reaction scheme:
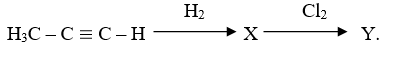
(i) Draw the structures of compounds X and Y.
(ii) What happens when bromine water is added to compound X and Y respectively.
(iii) Explain the answer given in 2(c)(ii).
(d) Magnesium reacts with aqueous solution of an acid to liberate hydrogen gas.
Write the:
(i) half-reaction equations;
(ii) overall reaction equation.
[3 marks]
(e) (i) State two differences between a mixture and a compound.
(ii) Classify each of the following substances as an element, a mixture or a compound: quicklime; gold; soil.
An element:
A mixture:
A Compound:
Observation
Majority of the candidates responded to the question and their performance was average.
In part (a), few candidates calculated the number of atoms that are in 10.0 g of CaCO3.
In part (b), majority of the candidates could not write a balanced equation to show the acidic nature of C2H2 when reacted with sodium.
In part (c), majority of the candidates could not draw the structures of the compounds X and Y respectively.
In part (d), majority of the candidates could not write the half-reaction equation when magnesium reacts with aqueous solution of an acid to liberate hydrogen gas.
In part (e), majority of the candidates stated the differences between a mixture and a compound.
The expected answers include:
(a) Molar Mass of CaCO3 = 40 + 12 + 3 (16)
= 100 g mol-1
:. 10.0 g CaCO3 = 10/100
= 0.1 mol
no. of atoms per molecule = 5
⇒ no of atoms in 10.0g CaCO3 = 5 x 0.1 x 6.02 x 1023
= 3.01 x 1023 atoms
(b)(i) I. C2H2 + 2Na → Na2C2(s) + H2(g) (2)
Or 2C2H2 + 2Na → 2C2HNa + H2
II. 2C2H5OH + 2Na → 2C2H5ONa(s) + H2(g)
(ii)
I. Sodium Carbide / Sodium ethynide
II. Sodium ethoxide
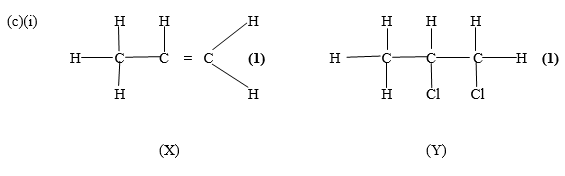
(ii) Compound X decolourises bromine water but compound Y does not decolourise bromine water.
(iii) Because compound X is an unsaturated compound and compound Y is a saturated compound
(d)(i) Mg(s) → Mg2+(aq)+ 2e- (1)
2H+(aq) + 2e- → H2(g) (1)
(ii) Mg(s) + 2H+(aq) → Mg2+(aq) + H2(g)(1)
(e)(i)
Mixture |
Compound |
- Homogeneous or heterogeneous |
- Only homogeneous |
(ii) quick lime – compound
Gold – element
Soil – mixture
