Question 3
(a) Explain briefly why each of the following statements of Dalton’s Atomic Theory
were modified:
(i) all elements are made up of small indivisible particles called atoms;
(ii) atoms combine in small whole numbers to form compounds;
(iii) atoms of the same element are alike in every aspect;
(iv) the atom can neither be created nor destroyed.
[4 marks]
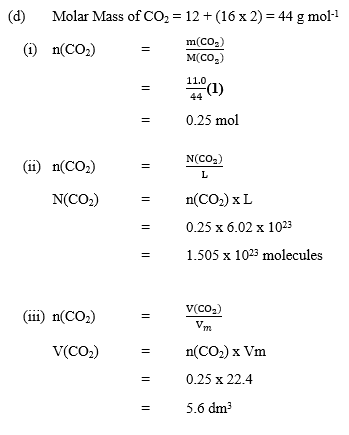
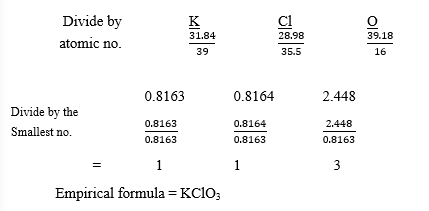
(b) A compound X is found to contain 31.84% potassium, 28.98% chlorine and the rest being
oxygen. Determine the empirical formula of X.
[O = 16.0; Cl = 35.5, K = 39.0]
[5 marks]
(c) (i) State one major industrial application of each of the following separation
techniques:
(I) fractional distillation;
(II) crystallization;
(III) sieving.
Observation
Majority of the candidates responded to this question, and their performance was above average.
In part (a), majority of the candidates explained why the Dalton’s Atomic Theory was modified.
In part (b), majority of the candidates correctly determined the empirical formula of X in the compound.
In part (c), majority of the candidates stated one major industrial application of fractional distillation, crystallization and sieving.
The expected answers include:
(a)(i) Because of the discovery of protons, neutrons and electrons.
(ii) Large organic molecules contain thousands of atoms.
(iii) The discovery of isotopes.
(iv) Nuclear reactions show that atoms can be formed or destroyed.
(b) Percentage of O2 = 100 – (31.84 + 28.98)
= 39.18%
(c)(i)
I - Petroleum refinery
- Purification of organic compounds
- Purification of water
- Separating water and ethanol
II - Manufacture of drugs/pharmaceutical industry
- Sugar production
- Salt production
III - Mining of solid materials
- Production of powdered food products
- Food industries
- Water purification
(ii) I - magnetic attraction
II - (solids of different) particle sizes
III - (miscible liquids with) close boiling points