Question 2
Differentiate between a partnership and a co-operative form of business under the following headings:
- Formation;
- Ownership;
- Capital;
- Management.
- Employers’ Association;
- Consumers’ Association.
Observation
Most candidates who attempted this question performed very well in part (a) of the question while for part (b), they could not state the reasons. Some stated the reasons for employee association while other could not state the reasons for the existence of these associations.
The expected responses to the question include:
(a) Differences Between a Partnership and a Co-operative Form of Business
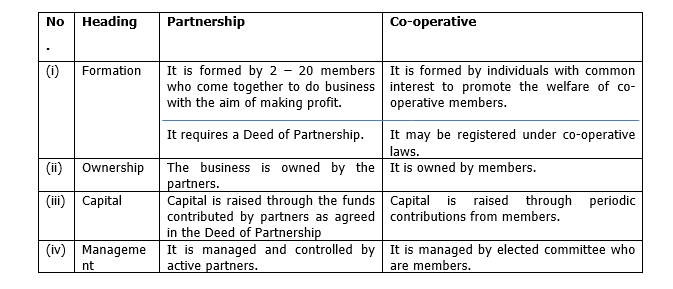
(b) Reasons for the Existence of Employers’ Association and Consumers’ Association
- Reasons for the Existence of Employers’ Association
- To provide a platform by employers to come together with a view to harmonising their interests.
- To provide enabling environment for their employees to carry on their assignments.
- To reconcile the wages and salaries of employees in the same line of business.
- To deal with industrial relations matters through collective bargaining/developing healthy and stable industrial relations.
- To serve as a pressure group to advise government to change its unfavourable policies towards members.
- To disseminate information that will better the members’ welfare, investments and growth in business.
- To provide the machinery for nominating suitable employers’ representation at conferences.
II Reasons for the Existence of Consumers’ Association
- To eliminate deceptive weights and measures from unscrupulous producers.
- To encourage consumers to be cautious of false and misleading advertisement.
- To help eliminate exploitation of consumers by producers and middlemen.
- To enhance steady and uninterrupted supply of goods and services.
- To demand for high quality goods and services from producers and service providers.
- To protect consumers from harmful, substandard or inferior goods from producers or importers.
- To ensure that consumers’ satisfaction is always realised.
- To conduct educational programmes that will benefit consumers.
