Question 1
-
(a) Define rectification.
(b) Figure 1 is a rectifier circuit diagram.
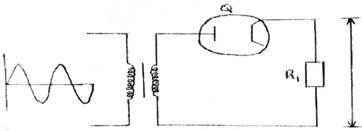
Figure 1- Identify the component labelled Q.
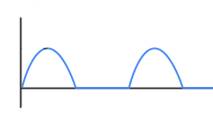
- Sketch the output waveform.
(c) Component Q in Figure 1 can be replaced with a semiconductor equivalent to perform the `same functions.
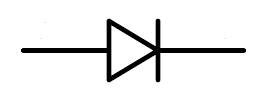
i. Draw the circuit symbol of the equivalent component.
ii. State two advantages of this equivalent component in 1 (c)(i) over Q
Observation
The expected responses were:
- Rectification is the conversion of alternating current to pulsating direct current.
(b) (i) Vacuum tube diode | Thermionic diode | diode
(ii) Output waveform
(c) (i) Semiconductor diode / PN junction diode
(ii) Advantages of semiconductor diode over vacuum tube diode
- It is more portable / smaller in size / not bulky
- Less fragile / more rugged
- Faster response/transient time
- Less power consumption
- Readily integrated
- Lighter in weight
- Cheaper | less expensive
Question 1 required candidates to define rectification and identify the parts of a rectifier. The Chief Examiner reported that a good number of the candidates responded well..
