Question 10
Part II. Candidates are expected to answer any three questions from this part.
- State two differences between a sound wave and a radio wave.
- Explain why a vibrating tuning fork sounds louder when its stem is pressed against a table top than when held in air.
.
- State two conditions necessary for the:
- production of stationary wave in a medium;
- formation of interference wave patterns;
- occurrence of total internal reflection of a wave.
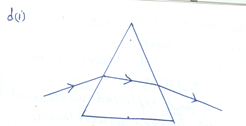
- A ray of light is incident on one face of an equilateral glass prism.
- Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the ray through the prism.
- Calculate the refractive index of the glass if the angle of minimum deviation is 41o.
Observation
Part(a). This was a popular question among the candidates and was treated with ease by virtually all the respondent. Performance was good.
Part (b): This question also evokes application of basic principles of physics. Many candidates were unable to explain the demand of the question. Many stated that the louder sound heard was due to the table vibrating in resonance with the tuning fork and so they lost marks. Performance was low.
Part (c): Almost all the candidates scored the full marks in their part. Performance was good.
Part (d): Quite a number of the candidates failed to trace the path of a ray through the prism correctly. This reflected poor grasp of refraction in glass prism. Omission of arrow(s) on the rays also led to loss of mark. The formula for calculating refractive index for a triangular glass prism eluded most candidates. Performance was low.
The expected answers are:
(a) . Sound wave and radio wave
Difference must match to score.
Sound wave Radio wave
- Is a mechanical wave Is an electromagnetic wave
- Is longitudinal Is transverse
- Has speed less than speed of light Has speed equal to that of light
- Requires a material medium for propagation/ Does not require a material medium for propagation/can
cannot travel through vacuum travel through vacuum.
(b) Vibrating turning fork
The vibrating tuning fork forces the table top to vibrate. The table top has a much larger area and is therefore in contact with a larger volume of air undergoing vibration. Hence, sound heard is louder.
(c)(i) Production of stationary wave
- two waves must be travelling in opposite directions.
- incident and reflected waves must have the same frequency/wave length.
- incident and reflected wave must have equal amplitude
- there must be superposition
- there must be a barrier.
(ii) Interference wave patterns
- two sources must be involved
- the two sources must be coherent / have a constant phase difference as well as the same frequency and amplitude.
- the waves that are interfering must have the same amplitude
- the distance between the sources must be of the order of the wavelengths of the waves.
(iii) Total internal reflection
. - The wave must be travelling from a denser medium to a less dense medium
- The angle of incidence of the wave in the denser medium must be greater than the critical angle for the medium.