Question 9
(a) Give three examples of thermometric properties
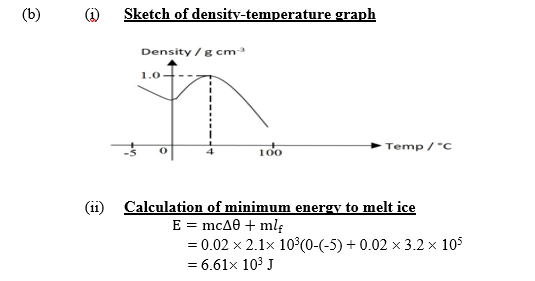
(b) A quantity of water of mass 20 g at -5oC was gradually heated until it finally boils.
(i) Sketch a graph of density against temperature for the heating process.
(ii) Calculate the minimum energy required to melt the ice.
[ specific heat capacity of ice = 2.1 x 103 J kg-1,Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 3.2 x 105 J kg-1]
(c) Define each of the following terms associated with a simple machine:
(i) load;
(ii) velocity.
(d) State whether or not velocity ratio is affected by frictional forces and give the reason for your answer.
(a) Give three examples of thermometric properties.
(b) A quantity of water of mass 20 g at -50C was gradually heated until finally boils.
(i) Sketch a graph of density against temperature for the heating process.
(ii) Calculate the minimum energy required to melt the ice.
[ specify heat capacity of ice = 2.1 x 103 J kg-1 K-1, Specify latent heat of fusion of ice = 3.2 x 105 J kg-1]
(c) Define each of the following terms associated with a simple machine;
(i) load;
(ii) velocity ratio.
(d) State whether or not velocity ratio is affected by frictional forces and give the reason for your answer.
Observation
(a) Examples of thermometric properties
Change in :
- Volume
- Resistance
- Length
- Pressure
- Emf
- Colour
(c) Definition of terms
(i) Load: The force overcome (by the effort applied) in a simple machine.
OR
The force overcome when work is done.
(ii) Velocity Ratio : The ratio of effort distance to load distance.
(d) It is not affected by frictional force
Reason : It is a ratio of distances.
