Question 1
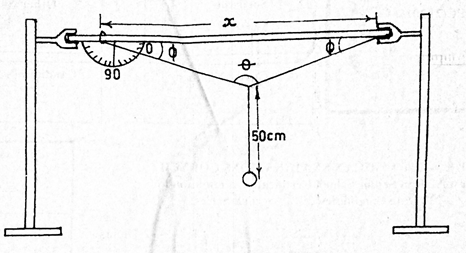
A meter rule is suspended horizontally by two clamps as illustrated in the diagram above. One end of the string is tied to the meter rule at the 5 cm mark and the other end is tied to the 95 cm mark. A simple pendulum of length 50 cm is suspended at the mid point of the string on the meter rule.
The angle Φ between the string and the meter rule is measured and recorded. The pendulum bob is set into simple harmonic motion and the time t for 20 complete oscillations is measured and recorded. The procedure is repeated for four other values of x.
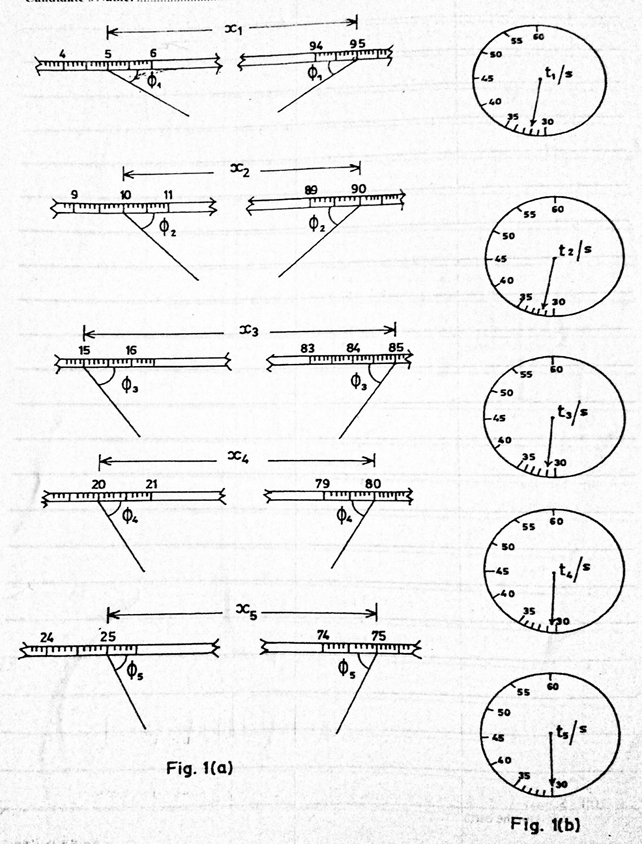
Fig. 1(a) shows the values of distances xi and the corresponding values of Φi
Fig.1(b) shows the corresponding time ti, where i = 1,2,3,4 and 5.
(i) Measure and record the values of the distances xi
(ii) Read and record the values of the angles Φi
(iii) Read and record the corresponding values of the time ti
(iv) In each case, evaluate:
(α) θ = 180 – Φ;
(β) cos θ;
(γ) T and T2.
(v) Tabulate your readings.
(vi) Plot a graph with T2 on the vertical axis and cos θ on the horizontal axis.
(vii) Determine the slope, s, of the graph.
(viii) Determine the intercept, c, on the vertical axis.
(ix) State two precaution that are necessary to ensure accurate results when performing this experiment.
(b) (i) Why is a spherical bob preferred to bobs of other shapes for use in the experiment?
(ii) State two reasons why acceleration of free fall due to gravity varies from place to place on earth’s surface.
Observation
Part (a) Candidates performance was below average. Majority of the candidates failed to evaluate cos θ correctly. Also, candidates wrongly measure xi on the diagram instead of reading the differences between points where the string was tied; the time ts of 20 oscillation was not read to 1 d.p and calculated T2 to 1 d.p.
Part (b) The question was fairly attempted. Majority of the candidates could not give correct reason why spherical bob is preferred to bobs of different shape.
The expected response:
- Five values of x correctly measured and recorded in cm (Deduct ½ mark for each wrong or missing value).
- Five values of ɸ correctly measured and recorded within tolerance of ± 1o (Deduct ½ mark for each wrong or missing value).
- Five values of t correctly read and recorded to at least 1 d.p and within
tolerance of ± 0.1 s
- (Deduct ½ mark for each wrong or missing value).
- Five values of θ = (180-2ɸ) OR 180 - (ɸiL + ɸiR) correctly evaluated (Deduct ½ mark for each wrong or missing value).
- Five values of cos θ correctly evaluated to at least 3 d.p (Deduct ½ mark for each wrong or missing value).
- Five values of T correctly evaluated to at least 2 d.p (Deduct ½ mark for each wrong or missing value).
- Five values of T2 correctly evaluated to at least 3 s.f (Deduct ½ mark for each wrong or missing value).
- Composite table showing at least x, ɸ, θ, cos θ, t, T and T2
- Plot a graph using reasonable scales
- Draw line of best it
- Determine the slope and intercept of the graph
- State any two of the following precautions.
e.g
- Ensured that small angle of displacement of bob was used
- Noted/corrected zero error in stopwatch/metre rule
- Avoided parallax error in stopwatch/metre rule/protractor
- Ensured metre rule firmly clamped/fixed
- Avoided conical oscillations
- Avoided draught
- Ensured retort stands are firm/rigid
- Ensured bob does not touch the table while swinging
- Repeated readings stated
In part b, the expected answers are:
b(i) Reasons for Using Spherical bob Over Others [02]
- It experiences least damping effect/low air resistance.
OR
- Offers minimal surface area to air resistance.
(ii) Reasons for the difference in acceleration due to gravity on earth’s surface
- Distance of object from the centre of the earth/shape of the earth/earth is not a sphere/earth has elliptic shape/earth is a geoid
- Effect of rotation
- Change in latitude
- Change in altitude
- Variation in the density of surface rock/irregularities in layers of rocks beneath the surface of the earth
