Alternative A
Question 1A
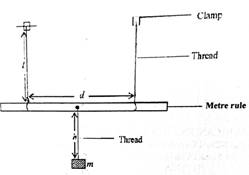
You are provided with a set of masses. Two metre rules, a piece of thread, two retort stands and clamps, a stop watch, split corks and a weighing balance.
Use the diagram above as a guide to perform the experiment.
- Measure and record the mass M of the metre rule.
- Suspend the metre rule, whose mass has been measured, by means of two vertical strings of equal lengths, l = 70cm.
- Make the separation between the threads, d = 80cm.
- Suspend a mass m = 20 g from the mid-point of the metre rule by means of a thread such that the distance between the mass and the rule, h = 15 cm.
- Displace the ends of the metre rule in a horizontal plane in opposite directions. Release the rule to perform horizontal oscillations.
- Determine the time, t for 20 oscillations.
- Evaluate the period T, T2 and T-2 .
- Repeat the procedure for four other values of m = 30g, 50g, 70g and 100g keeping the values of h, d and l constant. In each case, determine t and evaluate T, T2, and T-2.
- Tabulate the results.
- Plot graph with T2 on the vertical axis and m on the horizontal axis.
- Determine the slope s, of the graph.
- State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results.
(b) (i) Define the period of an oscillatory motion.
(ii) State two difference between mass and weight.
Observation
Part (a) Candidates performance was below average. Many candidates did not displace the ends of the meter rule in a horizontal plane in opposite direction, hence, arrived at the wrong trend of values.
Part (b) The question was fairly attempted.
The expected response:
1. (a) OBSERVATIONS
(i) Mass, M of metre rule correctly recorded to at least 1 d.p. in g.
(ii) Five values of m correctly recorded in g.
(iii) Five values of t correctly read and recorded to at least 1d.p in s and in trend.
Trend: As m increases, t decreases.
(iv) Five values of T correctly evaluated to at least 2 d.p
(v) Five values of T2 correctly evaluated to at least 3 d.p
(vi) Five values of T-2correctlyevaluated to at least3d.p.
(vii) Composite table showing at least m, t,,T, T2and T-2.
GRAPH
(i) Both axes correctly distinguished
(ii) Reasonable Scales
(iii) Five points correctly plotted
(iv) Line of best fit
SLOPE
(i) Large right-angled triangle
(ii) DT-2correctly determined
(iii) Dm correctly determined
(iv) ![]() correctly evaluated
correctly evaluated
PRECAUTIONS
- Avoided parallax error in reading metre rule
- Noted/corrected/Avoided zero error on metre rule
- Avoided draught
- Ensured that support was rigid/firm
- Repeated readings shown on table
- Ensured smooth and regular oscillations in a horizontal plane
- Ensured threads were firm /tight
NB: Conical oscillations should not be accepted.
(b) (i) Definition of the period of an oscillatory motion
It is the time taken by a body to make one complete oscillation.
(ii) Differences between mass and weight
Mass |
Weight |
Mass is a scalar quantity |
Weight is a vector quantity |
Mass is constant |
Weight varies |
Mass is the amount of matter contained in a body |
Weight is the force a body exerts on its support |
S.I unit of mass is kg |
S.I unit of weight is N |
Mass is a fundamental quantity |
Weight is a derived quantity |
Mass is measured with a chemical/beam balance |
Weight is measured with a spring balance |
