Question 4
Question 4
(a) Define:
(i) Modulation
(ii) Modulation index
(b) State two:
(i) Types of modulation;
(ii) Reasons modulation is important in electronic communication.
(c) A 100,000KHz carrier having an amplitude of 100v is amplitude modulated by 10KHz audion signal having an amplitude of 20v. calculate the
(i) Percentage modulation;
(ii) Side band frequencies.
Observation
The expected responses were:
(a) (i) Modulation is the process by which some characteristics of high frequency signal (carrier) is varied in accordance with the instantaneous value of a low frequency signal (modulating).
(i) Modulation index (m) is a measure of the extent of modulation done on a carrier wave. Modulation index is the ratio of the amplitude of the modulating signal to the amplitude of the carrier signal.
![]()
(b) (i) Types of modulation
- Amplitude modulation (AM)
- Frequency modulation (FM)
- Phase modulation (PM)
(ii) Reasons modulation is important in electronic communication
- for efficient transmission.
- to reduce noise and interference.
- to reduce antenna heights to practical limits.
- to achieve long distance communication of low frequency message.
(c) (i) Percentage modulation = ![]()
Where Am = 20V and Ac = 100V
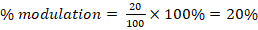
(ii) Sideband frequencies,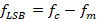
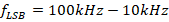
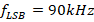
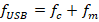
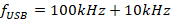
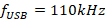
The Chief Examiner reported that the candidates did fairly well in this question.
