Question 3
(3)
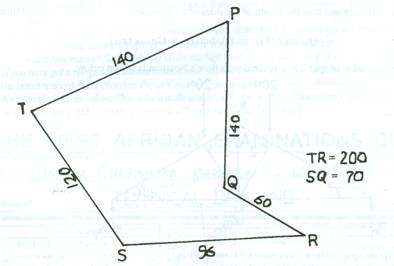
The figure above shows an irregular pentagon SRQPT.
- Construct half full size of:
- the given pentagon;
- a triangle equal in area to the pentagon, using SR extended as the base;
- a square half the area of the triangle in 3(a)(ii).
- Measure and state the length of the square in 3(a)(iii).
Observation
Candidates were required to reduce the given polygon to half the area in square and then measure and state the length of the half square.
Most of the candidates who attempted this question did not follow the required step. Thus candidates performance was poor.
Candidates were expected to do the following:
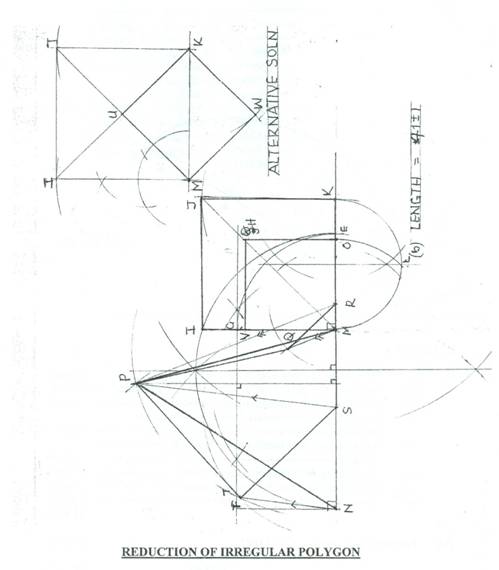
REDUCTION OF IRREGULAR POLYGON
(A) CONSTRUCTION OF POLYGON
(i) draw line SR as base;
(ii) locate point T and join TS;
(iii) locate point Q and join OR;
(iv) locate point P and join PT and PQ;
- draw to scale half full size.
(B) CONVERSION OF POLYGON TO TRIANGLE
(i) extend line SR on both sides;
(ii) join P to S and draw a line from T parallel to PS to locate point N;
(iii) join P to R and draw a line from Q parallel to PR to locate point M;
(iv) draw lines PN and PM to complete triangle PNM.
(C) CONVERSION OF TRIANGLE TO RECTANGLE
(i) draw a perpendicular from P to line SM;
(ii) bisect the perpendicular;
(iii) draw perpendiculars at points N and M to complete the rectangle NMGF.
(D) CONVERSION OF RECTANGLE TO SQUARE
(i) use radius MG and arc to locate point E;
(ii) bisect NE and draw a semi-circle on NE;
(iii) extend MG to locate point I on the semi-circle;
(iv) use MI to draw the square MKJI.
(E) REDUCTION OF SQUARE TO HALF FULL SIZE (METHOD 1)
- bisect MK and draw semi-circle on MK to locate point L;
- use ML as radius and describe an arc OL to locate point O on MK;
- draw half full size of the square MOHV.
(F) REDUCTION OF SQUARE TO HALF FULL SIZE (METHOD 2)
- join the diagonals MJ and KI to intercept at U;
- use radius MU to locate point W from points M and K;
- for drawing half full size of the square MWKU.
- Measure and state the length of side of half full size of the square produced.
The solution is shown below: