Question 5
(a) Table 3 contains some symptoms of faults in the lighting system of a motor vehicle.
Table 3
Symptoms |
Possible fault |
Headlight out of correct aiming |
(i) |
(ii) |
|
(iii) |
|
Non-working lights |
(i) |
(ii) |
|
(iii) |
|
Dim lights |
(i) |
|
(ii) |
|
(iii) |
Complete Table 3 with three possible faults for each symptom.
(b) Fig. 4 is a diagram of a type of automobile bulb.
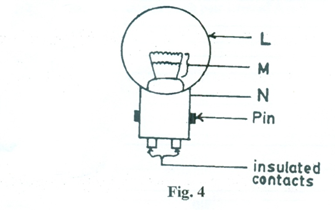
(i) Identify the parts labelled L, M and N.
(ii) State the purpose of the pins.
(iii) State two areas in the lighting system of automobiles where the bulb is used.
Observation
(a) Table 3
Symptoms |
Possible fault |
Headlight out of correct aiming |
Faulty suspension |
Damage to body panels |
|
Loose fittings |
|
Incorrect adjustment |
|
Non-working lights |
Blown bulbs |
Blown/burnt fuse |
|
Broken/loose wiring/connections |
|
Relay not working |
|
Corrosion in light units |
|
Switch not making contact |
|
Dim lights |
Low current from battery |
Loose battery terminal |
|
Weak battery cell |
|
High resistance in circuit |
|
Low alternator output |
|
Discoloured lens or reflectors |
(b) (i)
L – glass envelope
M – filament/double filaments
N – ground shell/earth
(ii) To hold the bulb in place when fixed in lamp holder
(iii) Two areas in the lighting system where the bulb is used
- Brake light
- Rear light
- Head light
Majority of the candidates that attempted Question 5 showed a good understanding of the topic.
