Question 2
- (a) (i) Define the first ionization energy of an element.
(ii) Consider the following table and use it to answer the questions that follow.
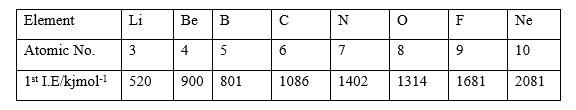
Explain briefly why the first ionization energy of B is less than that of Be despite the fact that the atomic number of B is greater than that of Be.
[8 marks]
(b) When Titanium chloride was electrolysed by passing 0.12 A current through the solution for 500 seconds, 0.015 g of titanium was deposited. What is the charge on titanium ion? [1F = 96500 C, Ti = 48.0] [6 marks]
(c) (i) Aluminium can be obtained by the application of electrolysis. State the electrolyte which yields aluminium or electrolysis.
(ii) Name two major factors which would favour the sitting of an aluminium smelter in a country.
[4 marks]
(d) (i) Define the term paramagnetism.
(ii) Consider the following ions:
24Cr2+, 24Cr6+
- Deduce the number of unpaired electrons in each of the ions.
- State which of the ions will have a greater power of paramagnetism.
- Give a reason for the answer stated in 2(d)(ii)(II).
[7 marks]
Observation
This question was popular among the candidates and their performance was average.
In part (a), majority of the candidates defined the first ionization of an element correctly.
In part (b), majority of the candidates could not calculate the charge on the titanium ion.
In part (c), majority of the candidates could not state the electrolyte which yields aluminium on electrolytes. However, they named two major factors which would favour the siting of an aluminium smelter in a country.
In part (d), few candidates defined paramagnetism correctly. However, they could not state which of the ions will have greater power of paramagnetism.
The expected answers include:
(a) (i) - Is the energy required to remove one electron from a mole of a gaseous atom
OR
- Is the minimum energy required to convert one mole of a gas of atom into one mole of a gaseous plus 1 ions
(ii) 4Be : 1s2 2s2
5B : 1s2 2s2 2p1
The electron to be removed from Be is in the 2s orbital which is closer to the
Nucleus nuclear attraction is greater hence first ionization energy is greater
but the electron to be removed from B is in the 2p orbital which is farther away from the nucleus, hence nuclear attraction is weaker hence first ionization energy is smaller.
OR
2p has less energy than 2s
So it is easier to remove an electron from 2p as the nuclear charge is weaker in 2p because 2p is further away from the nucleus. Hence, first ionization energy is small.
(b) Q = It
Q = 0.12 x 500
= 60 C
96500 = 1 F
= 60 C liberates 0.015 g
∴ 96500 will liberate 96500 x 0.015
60
= 24 g
n(T1) = m
M
= 24
48
= 0.5 mol
1 F ≡ 0.5 mol
∴2F ≡ 1 mol
hence charge = + 2
Alternative A
Q = It
= 0.12 x 500
= 60 C
0.015 g of Ti is deposited by 60 C
∴48 g will be deposited by = 60 x 48
0.015
= 192000 C
96500 C 1 mole of electron
∴192000 C = 1 x 192
96500
= 1.989
≈2.0 moles of electron
∴charge on Ti ion is + 2
Alternative B
m = 1t
M nF
n = M1t
mF
= 48 x 0.12 x 500
0.015 x 96500
= 1.989 ≈ 2
∴ Change on Ti ion is +2
(c) (i) Alumina (Al2O3) mixed with molten cryolite (Na3AlF6)
(ii) - abundant deposits of bauxite
- cheap source of electricity
(d) (i) Is the ability of a substance to be attracted strongly into a magnetic field
(ii) I. 24Cr2+ - 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p63d4
unpaired electrons = 4
24Cr6+ - 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6
unpaired electrons = 0
II. 24Cr2+
III. the greater the number of unpaired electrons in the 3d – orbital, the
greater the paramagnetism.
