The question was attempted by most candidates and the performance was fair.
In(a)(i) and (ii), candidates correctly defined Arrhenius base as a substance which produces
hydroxyl (OH-) ions in its aqueous solutions and gave one example from among NaOH,
Ca(OH)2, KOH and NH40H (names were also accepted for the examples).
In(a)(iii),only few candidates correctly identified aqueous solutions of:
I. CI2H22011. as non - electrolyte;
II. NH3 as weak electrolyte;
III. NaOH as strong electrolyte.
In(a)(iv), most candidates could not write a balanced equation to represent the reaction between
CH3COOH and KOH. The expected answer from candidate was as follows.
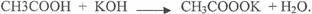
In part(b), candidates correctly calculated the volume ofHCl required for complete nuetrilization
of the NaOH thus:
CAVA = 1
CBVB
VA = CBVB =
CA 0.30 X 20
0.50 = 12.00cm3 (other method was accepted)
In parte c )(i) and (ii), candidates correctly gave the IUP AC name of each salt as sodium
oxochlorate (1) and magnesium hydrogen trioxocarbonate (IV) respectively.
In parte d)(i), candidates correctly defined standard solution as a solution whose concentration is
(accurately) known. However, most of them could not state the compound which is suitable or
the preparation of a standard alkaline solution nor give reason for their answer in (d)(ii).
The expected response from candidates was Na2C03, because it is stable in air/non deliquescent.
In(d)(iii), candidates correctly wrote an equation for the reaction between Fe and dilute HCl in I
and calculated the relative atomic mass of the metal in the given reaction in II as follows:
1. Fe(s) + 2HCl (aq) --+ FeCl2(aq) + H2(g)
II.
Number of moles of HCI used = 2.20 x 50.0
1000 = 0.11
Mole ratio ofHCl: Fe = 2: 1
:. number of moles of Fe used = 0.11 = 0.055 mole
2
0.055 mole of Fe = 3.08g
:. 1.0 mole of Fe = 3.08 x 1.0
0.055 = 56g
Relative atomic mass of Fe = 56 (other method was accepted)



