Question 2
(a) Use appropriate labelled diagrams to illustrate the following network topologies:
- Star topology;
- Bus topology;
- Ring topology;
(b) State one advantage of:
(i) star topology;
(ii) Bus topology;
(c) Use appropriate labelled diagrams to illustrate the following network topologies:
- Star topology;
- Bus topology;
- Ring topology;
(d) State one advantage of:
- Star topology;
- Bus topology;
(e) Give one disadvantage of:
- Bus topology;
- Ring topology:
Observation
The expected answer is:
- Network topologies
(i) star topology
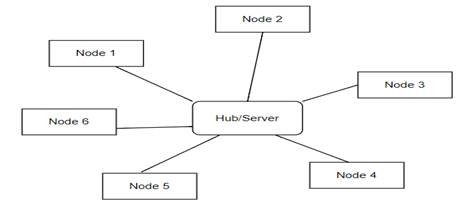
(ii) bus topology
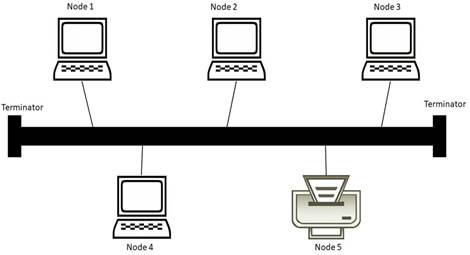
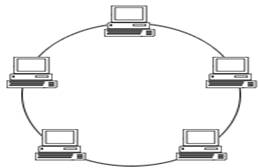
(iii) ring topology
- Advantages of:
(i) star topology
- Easy to install, configure and wire
- All cables run to a central hub reduced problem of cut cable
- It eliminates a number of lengthy cables runs if the hub is properly positioned
- Troubleshooting becomes easier due to shorter cable length
- when one workstation fails, other workstations do not fail because of the central hub.
- Better fault tolerance since no disruptions to the network when connecting or removing devices
- Easy to detect faults because the link is often easily identified
- User friendly: Easy to remove and add parts
- It is very reliable- if one cable or device fails then all the others will still work
- Highly efficient/It is high-performing as no data collisions can occur
- Less expensive because each device only needs one I/O port and wishes to be connected with hub of one link
- Robust in nature
- Centralized network
- No point-to-point connections
- Multiple stars can be created to extend the network’s reach/highly scalable
- Safe to use
- Easily manageable/Centralized management.
- It provides very high speed of data transfer.
- Multiple device types can be connected
- Some businesses may benefit from a wireless star topology system
- Multiple approaches can be taken with star topology systems.
- Low network traffic
- it is ideal for making a large network
(ii) Bus topology
- Easy to connect a computer or peripheral to a linear bus
- Requires less cable length than a star topology
- It works very efficiently well when there is a small network
- It is easy to connect or remove devices in this network without affecting any other device
- It is cost effective as compared to other network topology i. e. mesh and star
- It is easy to expand by joining the two cables together
- The length of cable required is less than a star topology.
- Easy to understand
- The failure of one station does not affect the rest of the network.
- No hubs or switches are required.
- Multiple nodes can be installed without difficulty.
- It is easy to set-up and extend bus network.
- Multiple peripherals can be supported through bus topology.
- Wiring terminators take no power requirements.
- Disadvantages of:
- bus topology
- It is not good for large networks
- Identification of problems becomes difficult if the whole network goes down
- Troubleshooting individual device issues is very hard
- Terminators are required at both ends of the main cable
- Additional devices slow the network down
- If the main cable is damage, the whole network fails or splits into two
- Packet loss is high
- It is very slow as compared to other topologies
- There is a limit on central cable length and number of nodes that can be connected
- Maintenance costs can get higher with time
- Efficiency of Bus network reduces, as the number of devices connected to it increases.
- It is not suitable for networks with heavy traffic.
- Security is very low because all the computers receive the sent signal from the source.
- A break in the backbone can cause an entire network to collapse
- Bus termination issues can lead to network issues.
- The computers may share data, but they don’t communicate.
- A T-connection failure immediately limits access.
- Not meant to be used as a stand-alone solution.
- Difficult to administer and troubleshoot
- A cable break can disable the entire network, and there is no redundancy
- One virus in the network will affect all of the systems
- Data traffic is high
- Limited cable length and number of stations
- It uses point-to-point mode of transmission.
- ring topology
- Due to the unidirectional ring all data being transferred over the network must pass through each workstation on the network which can make it slower
- The entire network will be impacted if one workstation shuts down
- The hardware (MAU’s) needed to connect each workstation to the network is more expensive than ethernet cards and hubs/switches.
- It is expensive
- Addition and removal of any node during a network is difficult and may cause issue in the network activity
- Difficult to troubleshoot the ring
- More problems caused by cut cabling because all cables do not run to a central hub as in a star topology.
- In order for all the computer to communicate with each other all computer must be turn on
- They are not scalable
- Unique wiring required
- More complex networking and operational protocol
It requires expert administration
- The network is highly dependent on the wire/cable which connects different component
- Data packets must pass through every computer between the sender and also a recipient side, therefore, this makes it slower
- All nodes require a token to send/receive data. So, all the computers have to wait for the empty token to reach them.
- Installing new workstations will disrupt the network
- The bandwidth of a ring topology gets shared on all links between devices.
- Each workstation connected will be able to access others information. This creates some security and privacy concerns since unauthorized people can easily intrude sensitive information.
The question tested candidates’ knowledge of networking.It was reported that the candidates who attempted this question showed relatively good knowledge of networking.
