Question 1
Figure 1 shows the circuit diagram of a full-wave bridge rectifier.
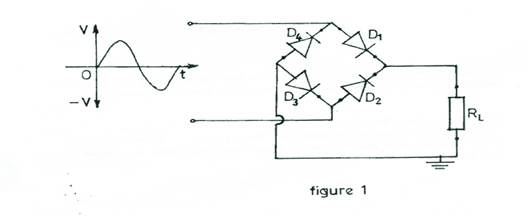
(a). Copy the diagram and indicate the direction of current flow during the
positive half cycle.
(b). State three advantages of a full-wave bridge rectifier.
Observation
The expected answers were:
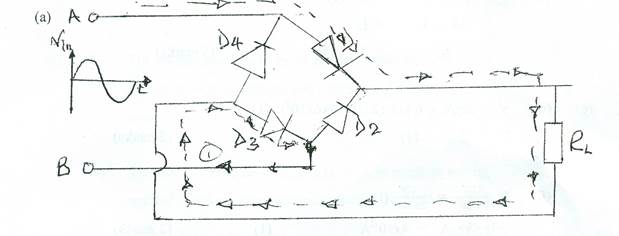
(b) Advantages of full-wave bridge rectifier
- Better ripple factor
- No centre-tap transformer is required
- Much smaller transformer is required
- Suitable for high voltage applications
- It has less Power/PlY rating per diode
The fundamental requirement in this question is the understanding of the fact that semiconductor rectifier diodes conduct only when positively biased. For the bridge rectifier therefore, only one pair of diodes will conduct in one half cycle of the sinusoidal varying input signal, whilst the second pair will conduct in the other half. It is important though to be able to identify which pair will conduct in which half cycle of the input signal as shown above.
