Question 10
-
- Define atomic spectra.
- Differentiate between emission spectra and absorption spectra.
-
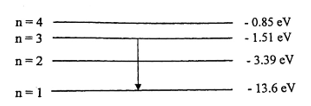
- The diagram above illustrates an electron transition from energy level n =
3 to n = 1. Calculate the:
- energy of the photon;
- frequency of the photon;
- wavelength of the photon
-
- Differentiate between soft x-rays and hard x-rays.
- Draw the circuit symbol for a p-n junction diode.
- Give the reason for doping a semiconductor material.
Observation
Part (a): Performance was poor. Many candidates failed to correctly define those concepts
signifying complete ignorance.
Part (b): Performance was good as many candidates were able to respond correctly to this
questions.
Part (c): Majority of the candidates correctly differentiated between soft x-rays and hard
x-rays and also gave correct reason for doping a semiconductor material but many could not give
the correct circuit symbol for a p-n junction diode.
The expected answer is
(a) (i) Definition of atomic spectra
The emission of light from a substance when its excited electrons move to lower energy level.
OR
Distinct/separate bright lines of light of definite frequency/wavelength (emitted from
vapourized atoms).
(ii) Differentiating between emission spectra and absorption spectra
Emission spectra is the pattern of light displayed when electrons jump from a higher energy
level to a lower energy level, while absorption spectra is the displayed pattern of wavelengths
absorbed by the gas.
(c) (i) Differentiating between soft x-rays and hard x-rays
Soft x-rays are those with longer wavelengths/lower penetrating power/ less energy while hard x-rays are those with shorter wavelengths/higher penetrating power/more energy.
(ii) Circuit symbol of p-n junction diode
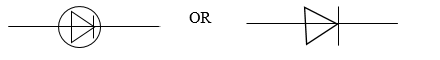 (iii) Reason for doping a semiconductor material
(iii) Reason for doping a semiconductor material
To increase the electrical conductivity/reduce electrical resistivity of the semiconductor.
