Question 10
(a) (i) Define each of the following terms as it relates to converging lenses:
(I) focal length;
(II) opticalcentre.
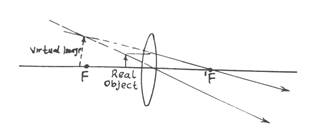
(ii) Draw a ray diagram to illustrate how a converging lens us used to produce a virtual image of an object.
(b) (i) Name the primary colours of light.
(ii) Match each primary colours to its corresponding complementary colour.
(c)
A ray passes symmetrically through a glass prism of angle 60O and refractive index of 1.5. Calculate the angle of:
- Incidence;
- Minimum deviation.
Observation
Part (a): Performance was fair. (i) Most candidates who attempted the question, though relatively few, got it right. (ii) Most candidates missed the correct position of the principal focus and position of the arrows when showing the converging lens.
Part (b): Performance was fair as many candidates were able tolist the primary colours but fail to list their corresponding complementary colours.
Part (c): Performance was fair.
The expected responses:
(a) (i) Definition of Terms
(I) Focal length of a converging lens: the distance between the optical centre and the principal focus.
(II) The (geometric) centre of the lens through which rays of light pass undeviated
OR
Optical centre of a converging lens: a point in the lens through which the principal axis passes and light rays pass undeviated
(ii)
(b) (i) Primary Colours of Light
- Red
- Blue
- Green
(ii) Match Each Primary Colours to its Corresponding Complementary Colour
- Red → cyan
- Blue→ yellow
- Green → magenta
(c) (i) Angle of Incidence
![]()
![]()
i = 48.6o
(ii) Angle of Minimum Deviation
![]()
![]()
Minimum deviation (Dm) = 37.2o
