Question 11
(a) (i) What is meant by the root-mean-square value of an alternating current?
(ii) Define impedance of an alternating current circuit.
(b) An electrical device rated 120 V, 60 W is operated on a 240 V, 50 Hz mains supply. The circuit has a capacitor connected in series with the electrical device and the supply. Calculate the capacitance of the capacitor. [ = 3.142]
(c) (i) Define the capacitance of a capacitor.
(ii)
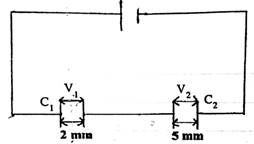
Observation
The circuit diagram above illustrates two capacitors of capacitance C1 and C2 connected in series across a 2 V sources.
- Obtain an expression for the total capacitance in terms of C2.
- Calculate the potential difference across each capacitor.
Part (a): This was another popular question among the candidates. Most of the candidates failed to correctly provide the meaning of root-mean-square value of an a.c. current.
Part (b): Performance was fair.
The expected responses:
(a) (i) Root-mean-square value
The direct current which has the same heating effect as the alternating current
(ii) Impedance of the circuit
The total opposition to the flow of an alternating current by both the resistive and reactive components.
OR
The overall opposition of a circuit consisting of resistor, inductor and capacitor to the flow of alternating current in the circuit
(b) ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Vc = 207.85
But Vc = IXc
207.85 = 0.15 x ![]()
C = 7,66μF
(c) (i) Definition of Capacitance of a Capacitor
The charge per unit voltage on the plates
(ii) (I) Expression for Total Capacitance
C1 and C2 are in series
Total capacitance CT = C1C2
C1+C2
Also C α 1
d
![]()
![]()
(II) Q = CTV
= ![]()
V2 = Potential across C2
V2 = ![]()
![]()
= 1.43 V
