Question 12
(a) (i) State the principal factor that determines the relatives stability of radioactive nucleus
(ii) Arrange the following radionuclides in the decreasing order of stability. Justify your answer: ![]() ,
,![]() and
and ![]()
(b) (i) Explain the term ionization potential .
(ii)
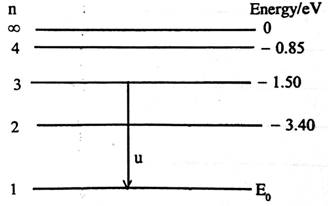
Observation
The diagram above illustrates energy levels in the hydrogen atom. EO is the energy of the ground state.
Part (a): This question was unpopular among the candidates. Performance was poor.
Part (b): Performance was poor. Few who attempted failed woefully.
Part (c): Performance was poor.
The expected answer is:
(a) (i) Principal Factor that Determines the Relative Stability of a Radioactive Nucleus
Neutron-proton ratio.
(ii) Arrangement of Radio Nuclides in Decreasing Order of Stability
![]()
![]()
![]()
Decreasing order of stability
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]()
(b) (i) Ionization potential
The minimum energy required to remove an electron completely from an atom
(ii) (I) Calculation of Eo
![]() OR
OR ![]()
![]()
![]() = -13.6 eV
= -13.6 eV
(II) Calculation of Ionization Potential
Ionization Energy = ![]()
= ![]()
= 13.6 eV
Therefore, Ionization potential = 13.6 eV
(c) (i) Explanation of the Statement
The minimum energy needed to remove an electron from the surface of sodium metal is 2.0 eV.
(ii) For sodium metal, ![]()
= 2.0 x 1.6 x 10-19 J
![]()
![]()
= 6.2 x 10-7 m
160nm = 160 x 10-9
= 1.6 x 10-7 m
Since 1.6 x 10-7 m is less than 6.2 x 10-7 m, photoelectrons would be emitted when light of 160 nm is shone on the metal surface
