Question 10
(a) (i) Why are parabolic mirrors suitable for use in headlamps of vehicles?
(ii) Draw a ray diagram to illustrate the answer in 10(a)(i).
(b)(i) State two applications of echoes.
(ii) An observer standing at a point, P, on the same horizontal ground as the foot, H, of a tower shouts and 1.20 s later, he hears the echo. He then moved to another point, Q, 40m from P, and shouts again but the echo was heard after 1.45 s. Calculate the:
(i) Distance between P and H;
(ii) Speed of sound in air.
(c) (i) Define the term absolute refractive index of a medium.
(ii) A piece of coin falls accidentally into a tank containing two immiscible liquids A and B as illustrated in Fig. 10.0.

Calculate the displacement of the coin when viewed vertically from above.
[refractive index of A = 1.3, refractive index of B = 1.4]
Observation
In question 10a, a large number of candidates correctly identified the reason for using a parabolic mirror as a car headlamp. However, several candidates drew a concave mirror instead of a parabolic mirror.
Question 10b saw most candidates performing well in identifying the applications of echo.
In question 10c, the majority of candidates accurately defined the absolute refractive index but struggled to calculate the displacement of a coin in a tank containing two immiscible liquids.
EXPECTED RESPONSES:
(a) (i) Reason for using a parabolic mirror
- They produce a parallel beam of light with the same intensity over a long distance.
(ii) Ray diagram
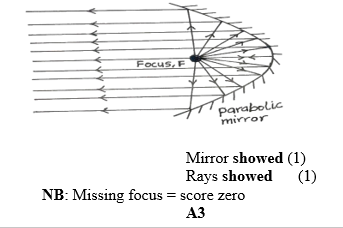
(b) (i) Applications of echo
- Location of ores/solid minerals
- Determination of the depth of the sea/ocean floor
- Echolocation/navigation
- Determination of the speed of sound
- Used in radars
- Used in MRI/ Ultrasound
- Location of wreckage
(ii) Calculation of distance and speed
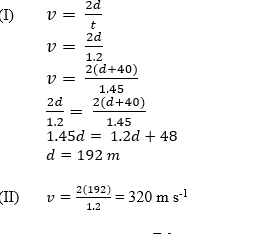
(c) (i) Definition of absolute refractive index
- The ratio of the speed of light in vacuum/air to the speed of light in the medium.
OR
- The ratio of the Sine of the angle of incidence in vacuum/air to the Sine of the angle of refraction in the medium.
[2 marks]
(ii) Calculation of displacement
(1)
= 0.092 m = 9.2 cm (½)
= 0.023 m = 2.3 cm (½)
The displacement from the bottom
(1)
= 0.092 + 0.023 = 0.115 m
= 11.5 cm (1)
