Alternative B
Question 1B

You are provided with a set of masses, a metre rule, a thread, two retort stands and clamps, a stop watch , a knife edge and spilt corks.
Carry out the following instructions using the diagram above as a guide.
- Determine the centre of gravity, C, of the metre rule using knife edge.
- Read and record the mass, M, of the metre rule written n the reverse side of it.
- Suspend the metre rule by means f two parallel threads of equal length, h = 70cm, with one at the 10 cm mark and the other at the 90 cm mark of the metre rule.
- Attach a mass m = 30 g firmly to the metre rule at C. ensure that the graduated face of the metre rule is facing upwards and that d = 80cm throughout the experiment.
- Set the metre rule into small angular oscillations about the vertical axis through its centre of gravity by displacing its ends in opposite directions.
- Determine the time, t, for 20 oscillations and evaluate the period T, T2 and T-2.
- Repeat the procedure for four other values of m = 40 g, 50 g, 60 g and 70 g.
- Plot a graph of T-2 on the vertical axis and m on the horizontal axis.
- Determine the slope, s, of the graph.
- Evaluate Q =
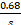 .
. - State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results.
(b) (i)Give two examples of simple harmonic motion other than the motion of a simple pendulum
(ii) Explain the term centre of gravity of a body.
Observation
Part (a) Majority candidates attempted this question. Performance was fair.
Part (b) Candidates response was satisfactory.
The expected response:
1 (a) OBSERVATIONS
- Value of C correctly measured and recorded to at least 1 d.p and within 50 ± 0.5 cm
- Value of M correctly recorded
- Five values of m correctly recorded in g.
- Five values of t correctly measured and recorded to at least 1d.p in s and in trend.
Trend: As m increases, t decreases
- Five values of T correctly evaluated to at least2 d.p.
- Five values of T 2 correctly evaluated to at least3 d.p
- Five values of T -2 correctly evaluated to at least 3 d.p
- Composite table showing at least m, t, T, T 2 and T -2
GRAPH
- Both axes correctly distinguished
- Reasonable scales
- Five points correctly plotted
- Line of best fit.
SLOPE
- Large right – angled triangle
- ∆ T-2 correctly determined
- ∆ m correctly determined
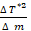 correctly evaluated
correctly evaluated
EVALUATION OF Q
Q = ![]()
Correct substitution
Correct arithmetic
PRECAUTIONS
- Ensured threads were firm /tight.
- Ensured supports of pendulum were rigid.
- Avoided parallax error on metre rule/stopwatch/ clock.
- Zero error was noted and corrected on metre rule/stopwatch/stopclock
. Ensured smooth and regular oscillations in a horizontal plane.
- Repeated readings shown on table.
- Avoided draught.
NB: Avoiding conical oscillation should not be accepted
b(i) Examples of simple harmonic motion other than simple pendulum.
- A body at the end of a spring performing vertical oscillations with small amplitude
- A floating rod/loaded test tube suspended in a liquid performing vertical oscillations with small amplitude.
- A liquid performing oscillations in a U-tube with a small amplitude.
- Vertical motion of a loaded spiral spring.
- Motion of a sounded/vibrating tuning fork.
- A vibrating loaded bar clamped to a bench / A vibrating cantilever.
- Motion of a see-saw.
- Motion of steel ball in a curved dish
