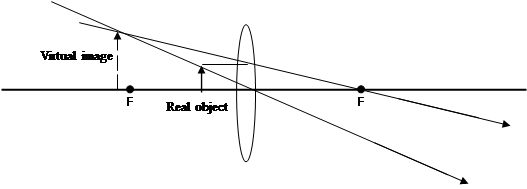Alternative B
Question 2B
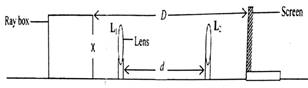
You have been provided with a ray box, a converging the lens, a lens holder, a screen, a metre rule, and half-metre rule.
Use diagram above as a guide to perform the experiment.
- Determine the approximate focal length, f, of the lens by focusing a distant object on the screen.
- Place the ray box and the screen such that the distance between the illuminated cross-wire and the screen, D = 150 cm.
- Place the lens at a position L1 where a sharp image of the cross-wire is obtained on the screen. Note L1.
- Move the lens to a position L2 to obtain another sharp image of the cross-wire on the screen. Note L2
- Measure the distance, d between L1 and L2
- Evaluate D2, d2 and D2 – d2
- Tabulate the results.
- Plot a graph with D2 – d2 on the vertical axis and D on the horizontal axis.
- Determine the slope, s, of the graph.
- Evaluate k =

- State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results.
(b) (i) Distinguish between a virtual image and a real image?
(ii) With the aid of a ray diagram, explain how a converging lens produces a virtual image.
Observation
Part (a) This question was another popular question. Candidates’ performance was fair. Candidates did not follow the instruction of setting the metre rule into small angular oscillation about the vertical axis through its centre of gravity thereby loosing marks.
Part (b) Candidates response was fair.
The expected response:
2 (a) OBSERVATIONS
- Value of focal length f correctly measured and recorded to at least 1 d.p in cm
- Five values of D correctly measured and recorded to at least 1 d.p in cm.
- Five values of d correctly measured and recorded to at least 1 d.p and in trend.
Trend: As D decreases, d decreases.
- Five values of D2 correctly evaluated.
- Five values of d2 correctly evaluated.
- Five values of (D 2 - d 2) correctly evaluated.
- Composite table showing at least D, d, D 2, d 2 and (D 2 - d 2).
GRAPH
- Both axes correctly distinguished
- Reasonable scales
- Five points correctly plotted
- Line of best fit.
SLOPE
- Large right – angled triangle
- ∆
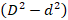 correctly determined
correctly determined - ∆ D correctly determined
 correctly evaluated
correctly evaluated
EVALUATION OF k
k = ![]()
ACCURACY
Based on k = f ± 10 % of the teacher’s value
PRECAUTIONS
- Lens was placed vertically/ erect(in its holder).
- Avoided Parallax error on metre rule..
- Avoided zero error on metre rule
- Cleaned surfaces of lens.
- Repeated readings shown on table.
b(i) Differences between real and virtual images
REAL IMAGE |
VIRTUAL IMAGE |
It can be focused/formed on a screen |
It cannot be focused/formed on a screen |
It is inverted/turned upside down |
It is erect/upright |
Formed by the actual intersection of light rays. |
Formed by the apparent intersection of light rays. |
(ii)